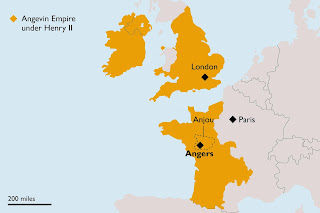
Well, England, of course, in which Henry had his grandest title of king, and also parts of Ireland and Wales. Through Henry's father, Geoffrey of Anjou, he was also Count of Anjou. Also, since Geoffrey took over Normandy not long before, Henry was Duke of Normandy. Moreover, because Henry married Eleanor of Aquitaine in 1152—who divorced the King of France to do so—he had Aquitaine.
The term "Angevin" was coined in 1887 by a British historian, based on "Anjou." Henry and his successors (sons Richard and John and John's son Henry III) would refer in documents to "our kingdom and everything subject to our rule whatever it may be" and never called it an empire or referred to themselves as Angevin. Technically, they were all Plantagenets.
Plantagenet was Geoffrey of Anjou's nickname. The plantagenet was the common broom, a flowering plant with bright yellow blossoms. Geoffrey was also known as Geoffrey the Handsome or the Fair. Perhaps his hair was lighter than typical, and the comparison to the golden flowers of the broom prompted the nickname. Even so, like the term "Angevin," it wasn't until Richard, 3rd Duke of York adopted Plantagenet as his family name during the Wars of the Roses that the term become attached to the whole hereditary line. It seems that Richard was linking himself to his ancestor Geoffrey in order to emphasize his proper place in the line of succession.
Extensive holdings on the continent (and perhaps spite, since Eleanor had abandoned being queen in France to become Queen Eleanor of England), made France a little hostile to the Angevin Empire. The problem created by Duke William of Normandy when he became King William of England in 1066 remained: how does a king of a country (England) react when he is likewise a lesser title (duke, count) in another country (France) and therefore subordinate to a king? That political oddity would define the English-French relationship for centuries.
It also calls into question the term "empire." To truly be an empire requires a centralized government and consistent laws and regulations throughout the territories. The varying laws and customs of the various Angevin territories were at odds with this definition.
Whether it was an empire like the Roman Empire or the medieval Holy Roman Empire, it didn't last more than a generation or two. Its demise will be the subject of the next post.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.