One was that the political power of Western Europe had recently grown; kingdoms were becoming more sophisticated with fewer border squabbles, and the church and the secular powers had the organizational ability to manage a large undertaking. Also, there was an eschatological air ever since the year 1000, and the end of the world could be nigh, sparking a religious fervor not previously seen. The end of the world in Biblical terms involved Jerusalem, and so freeing Jerusalem from infidels was important. A request from Alexius I Comnenus of Constantinople to get help from the West with his infidel problems was a catalyst for Urban II to declare this undertaking.
Assembling armies takes time, however, and joining the Crusade was expensive. There was no large standing army in any country capable of taking on such a huge military operation, so citizens from all walks of life were recruited. The prospect of a plenary indulgence from the pope that would remove the need for penance was a strong inducement to join. Individuals sold goods and sought donations to be able to afford food, armor, weapons, passage, etc.
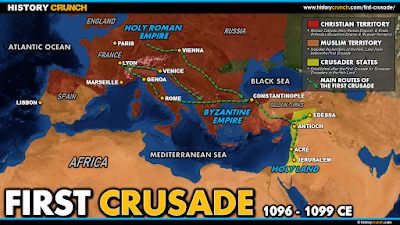
The main forces (there were four major organized groups) were ready to depart Europe in August 1096. A fifth and smaller force led by the King of France's brother, Hugh of Vermandois, left early and was shipwrecked in the Adriatic. (There was also an impatient "People's Crusade" that left early and, well, see the result here.)
The major group was led by Godfrey of Bouillon (1060 - 1100), the duke of Lower Lorraine. Much of the story of the First Crusade relies on his actions. We can look at how the Crusade went through the point of view of the first European "King of Jerusalem" next time.