We have seen how some sources, such as the University of Paris, spoke against astrology's predictive uses not because it believed they were in error, but because they were believed to contravene God's wishes for human beings. There were others who objected to the reliance on astrology because they could not believe that it was likely to work.
Ibn Qayyim Al-Jawziyya (1292-1350) was a Sunni Islam theologian and commentator on the Qu'ran. Not given to flights of fancy, and accustomed to arguing the details of the law, he put a critical lens on astrology. One of the lynch pins of his refutation of astrology came from the fact that hundreds of stars were not included in astrological calculations. Astrologers told him that the stars were too far away and to small to matter. To Al Jawziyya, this was an intolerable double-standard:
And if you astrologers answer that it is precisely because of this distance and smallness that their influences are negligible, then why is it that you claim a great influence for the smallest heavenly body, Mercury? Why is it that you have given an influence to al-Ra's and al-Dhanab, which are two imaginary points?Astrologers accepted at the time, through their calculations, that the stars appeared small because they were far away, but were actually enormous compared to the world. They also knew that the Milky Way was "a myriad of tiny stars packed together in the sphere of the fixed stars"; Al-Jawziyya said that it was impossible to know what effect, if any, they would have. Astrology had too many variables, and was just so much guesswork.
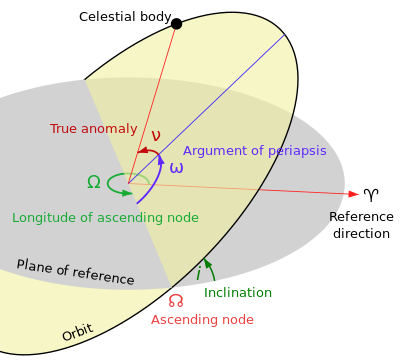
What were the "two imaginary points" mentioned in the above quotation? He was referring to "orbital nodes," the imaginary point in space where the line of "an orbit crosses the plane of reference to which it is inclined." Astrologers made much out of these points, which had no physical existence, and yet ignored actual physical stars. They neglected stars as being too small to matter, and yet put all their attention on planets that were a ridiculously small fraction of the size of a star. To the keen legal and theological mind of Al-Jawziyya, this suggested that astrology was not, in fact, based on any kind of rational thinking.