St. Anthony the Great is credited with being the first monk in that he did not just live an ascetic life, but also he removed himself from civilization and went into the desert. The eremitical (hermit) life appealed to many in the years to follow, but not everyone had the self-discipline to lead that kind of life. This is where Pachomius was needed.
St. Pachomius (c.292-348) was born a pagan. Drafted into military service by the Roman army, he noticed how Christians brought food to the conscripts. When he left the army a few years later, he investigated Christianity and converted in 314. After seven years as a hermit, he traveled to where St. Anthony was living, modeling his life after Anthony's solitary example. Then, however, a vision told him to create a community where others could join him.
Hermits had clustered together in the same area before, but Pachomius created an organized structure for monks who actually lived and worked together, holding their possessions in common and following a similar schedule. This style of monastic tradition is called cenobitic, a Latin word from the Greek words for "common" [κοινός] and "life" [βίος].
He created the first community shortly after this vision; the first person to join him was his brother John. Many more were to follow. Pachomius built nine monasteries, but the trend caught on: by the time of his death there were an estimated 3000 communities in Egypt. Pachomius was referred to as "Abba," [father], from which the terms "abbot" and "abbey" come. He also wrote the Rule of Pachomius, creating guidelines for communities. It is written in the Coptic (Egyptian) language.
Pachomius never was ordained as a priest. St. Athanasius visited him and wanted to ordain him in 333—Pachomius, like Athanasius, had proven to be a vocal opponent of Arianism—but Pachomius did not want ordination. He died on 9 May 348, presumably from plague.
09 May 2013
08 May 2013
Anthemius of Tralles
Anthemius of Tralles (c.474-c.557) was mentioned as one of the builders (along with Isidore of Miletus) of the new Hagia Sophia. We know much more about him than that, however, both about his talents...and his annoying pranks.
We have an anecdote about how he avenged himself on his neighbor, Zenon, by fashioning leather tubes that he ran to the joists of an upper room of Zenon's house, where Zeno used to entertain guests. We are told that Anthemius would, by running steam through the tube, create loud noises and vibration in he room, frightening the guests into thinking there was an earthquake. Also, he would flash incredibly bright light into Zenon's eyes with a concave mirror.
Possible? Well, he did write a treatise "On burning-glasses"; we don't have the treatise anymore, but enough of it existed in 1777 to be included in a work called Concerning wondrous machines by an L. Dupuy. He apparently studied and wrote on properties of mirrors and lenses, and supposedly described a camera obscura. He explained how to construct an ellipse using string, and he wrote a book on conic sections.
This intellectual excellence ran in the family. His father, Stephanus of Tralles, was a physician with five sons. Two of them followed in their father's footsteps, Dioscorus staying in Tralles and Alexander finding fame in Rome. The rest pursued different professions. Metrodorus became a grammarian in Constantinople; Olympius became an expert in Roman jurisprudence.
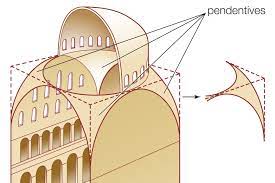
Anthemius' knowledge of conic sections and parabolas would have supported both his work on optics (known to the later "Second Ptolemy" Alhazen ibn al-Haytham) and his architectural aspirations when designing the dome of the new Hagia Sophia. He was able to create what is called a "pendentive": a design that allows a dome to be built onto a square base.
His success with Hagia Sophia led to him being also chosen—probably by Emperor Justinian—to design flood defenses at Dara in northern Mesopotamia.
We have an anecdote about how he avenged himself on his neighbor, Zenon, by fashioning leather tubes that he ran to the joists of an upper room of Zenon's house, where Zeno used to entertain guests. We are told that Anthemius would, by running steam through the tube, create loud noises and vibration in he room, frightening the guests into thinking there was an earthquake. Also, he would flash incredibly bright light into Zenon's eyes with a concave mirror.
Possible? Well, he did write a treatise "On burning-glasses"; we don't have the treatise anymore, but enough of it existed in 1777 to be included in a work called Concerning wondrous machines by an L. Dupuy. He apparently studied and wrote on properties of mirrors and lenses, and supposedly described a camera obscura. He explained how to construct an ellipse using string, and he wrote a book on conic sections.
This intellectual excellence ran in the family. His father, Stephanus of Tralles, was a physician with five sons. Two of them followed in their father's footsteps, Dioscorus staying in Tralles and Alexander finding fame in Rome. The rest pursued different professions. Metrodorus became a grammarian in Constantinople; Olympius became an expert in Roman jurisprudence.
Anthemius' knowledge of conic sections and parabolas would have supported both his work on optics (known to the later "Second Ptolemy" Alhazen ibn al-Haytham) and his architectural aspirations when designing the dome of the new Hagia Sophia. He was able to create what is called a "pendentive": a design that allows a dome to be built onto a square base.
His success with Hagia Sophia led to him being also chosen—probably by Emperor Justinian—to design flood defenses at Dara in northern Mesopotamia.
07 May 2013
The Dome of Holy Wisdom
The greatest church in the eastern Mediterranean was the Hagia Sophia [Greek Ἁγία Σοφία - "Holy Wisdom"] in Constantinople. The first church on the site was dedicated in 360 CE, and has served as an Eastern Orthodox Cathedral, as a Roman Catholic Cathedral (from 1204, when the Fourth Crusade captured Constantinople, until 1261), as a mosque (from 1453 until 1931), and as a museum (from 1931 until the present day). It was the largest church in the world until 1520, when the Seville Cathedral was built.
When the original church was burned down during rioting,* Emperor Justinian I ordered construction of the current building in the 530s. He employed the talents of two men—we would call them "architects," although contemporary documents refer to them as "mechanics"—named Isidore of Miletus and Anthemius of Tralles. He insisted that they make a flame-proof building, so they designed it with stone and brick-and-mortar, bound in some places by iron, but with no wood anywhere. There are other dangers than fire, however.
On 7 May 558, the dome of the Hagia Sophia collapsed during an earthquake. It was rebuilt by Isidore the Younger, a nephew of Isidore of Miletus. This time, the design included 40 ribs as support, and a dome that was six meters higher. Unfortunately for the dome, the walls were constructed of less brick and more mortar, and built too quickly—they should have let the mortar cure longer in each layer before adding the next—and were consequently not as strong. The new dome also experienced collapses. The current dome contains a north section of eight ribs and a south section of six ribs from the original.
*Constantinople had two political factions, called the Blues and the Greens; their rivalry frequently became violent, resulting in property damage
When the original church was burned down during rioting,* Emperor Justinian I ordered construction of the current building in the 530s. He employed the talents of two men—we would call them "architects," although contemporary documents refer to them as "mechanics"—named Isidore of Miletus and Anthemius of Tralles. He insisted that they make a flame-proof building, so they designed it with stone and brick-and-mortar, bound in some places by iron, but with no wood anywhere. There are other dangers than fire, however.
On 7 May 558, the dome of the Hagia Sophia collapsed during an earthquake. It was rebuilt by Isidore the Younger, a nephew of Isidore of Miletus. This time, the design included 40 ribs as support, and a dome that was six meters higher. Unfortunately for the dome, the walls were constructed of less brick and more mortar, and built too quickly—they should have let the mortar cure longer in each layer before adding the next—and were consequently not as strong. The new dome also experienced collapses. The current dome contains a north section of eight ribs and a south section of six ribs from the original.
*Constantinople had two political factions, called the Blues and the Greens; their rivalry frequently became violent, resulting in property damage
06 May 2013
Damascus - Some History
Dimashq.
دمشق.
Dimishe'.
al-Shām.
The City of Jasmine.
"Oldest continuously inhabited city in the world."
Damascus.
It was founded in the 3rd millennium BCE and (according to the Unesco World Heritage site) "has some 125 monuments from different periods in its history."
When Imad al-Din Zengi, the Prince of Mosul, laid siege to Damascus in 1138, Damascus resisted by allying with the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem (ruled at the time by Fulk V of Anjou [1089-1143]). The admirably tolerant Seljuq-Christian alliance turned back their common enemy. It was this conflict that prompted Raymond of Poitiers, Prince of Antioch, to send Bishop Hugh of Jabala to Pope Eugene III for aid. It was Hugh at the court of Pope Eugene whose mention of a Nestorian priest-king in the East started the legend of Prester John.
Saladin, the noble foe of Richard Lionheart, founded the Ayyubid dynasty, Muslim Kurds who ruled an independent Damascus. Saladin allowed pilgrimages to Jerusalem, with the understanding that the Crusaders would return home after fulfilling their Crusading vows. After Saladin's death in 1193, Damascus was ruled sometimes by Ayyubids from Damascus, sometimes by Ayyubids from Cairo.
By this time, Damascus was one of the western endpoints of the Silk Road. Damascus itself was known for crafts and cloth, and the cloth called damask was a specialty.
Independent Ayyubid rule ended in 1260 with a Mongol Invasion; when the Mongols left, Damascus was reduced to being a provincial capital of the Mamluk Empire of Egypt. A few generations later, the Black Death killed up to 50% of the population.
دمشق.
Dimishe'.
al-Shām.
The City of Jasmine.
"Oldest continuously inhabited city in the world."
Damascus.
It was founded in the 3rd millennium BCE and (according to the Unesco World Heritage site) "has some 125 monuments from different periods in its history."
When Imad al-Din Zengi, the Prince of Mosul, laid siege to Damascus in 1138, Damascus resisted by allying with the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem (ruled at the time by Fulk V of Anjou [1089-1143]). The admirably tolerant Seljuq-Christian alliance turned back their common enemy. It was this conflict that prompted Raymond of Poitiers, Prince of Antioch, to send Bishop Hugh of Jabala to Pope Eugene III for aid. It was Hugh at the court of Pope Eugene whose mention of a Nestorian priest-king in the East started the legend of Prester John.
Saladin, the noble foe of Richard Lionheart, founded the Ayyubid dynasty, Muslim Kurds who ruled an independent Damascus. Saladin allowed pilgrimages to Jerusalem, with the understanding that the Crusaders would return home after fulfilling their Crusading vows. After Saladin's death in 1193, Damascus was ruled sometimes by Ayyubids from Damascus, sometimes by Ayyubids from Cairo.
By this time, Damascus was one of the western endpoints of the Silk Road. Damascus itself was known for crafts and cloth, and the cloth called damask was a specialty.
Independent Ayyubid rule ended in 1260 with a Mongol Invasion; when the Mongols left, Damascus was reduced to being a provincial capital of the Mamluk Empire of Egypt. A few generations later, the Black Death killed up to 50% of the population.
05 May 2013
Lohengrin
 |
| Henry being offered the position of King of Germany, while working with his nets. (1900, Hermann Vogel) |
Henry (876-936) was the son of King Otto the Illustrious, Duke of Saxony. When his father died in 912, Henry proved to be an able ruler. In his lifetime, the empire assembled by Charlemagne was now divided into seven different kingdoms, none of them wanting to be ruled by the others. Henry strengthened the standing of Saxony and defended it able against territorial incursions from neighboring states, such as Franconia to the south.
Conrad I, Duke of Franconia, was Henry's rival for years over rights to Thuringia. When Conrad died in December 918, however, he told his nobles that Henry of Saxony was the right man to follow in a united Germany. At a meeting of nobles in 918, it was agreed that they would seek out the Duke of Saxony and ask him to lead. A delegation was sent to offer Henry their loyalty.
Henry, like many aristocrats of the Middle Ages, enjoyed hunting of all kinds. Henry was supposedly known for being an avid fan of hunting birds. He is supposed to have been hunting high up in the Hartz mountains and working at his nets when they found him, as portrayed in the picture above; hence the name Henry the Fowler.
No sooner was he enthroned than the Germans were invaded by the Magyars. In the process of countering it, Henry's forces took as hostage the son of the Magyar king, which paused the wars for many years. When the Magyar king asked for the return of his son, Henry offered him terms that were too good to pass up: Henry wanted a nine-year truce, during which he would pay 5000 gold pieces per year for there to be no threats from Hungary. The Magyar king agreed.
Henry spent the next nine years building up and drilling his army to make them a fearsome fighting force. He also built fortresses along his borders. When the Magyars tried to invade during the tenth year since the truce, Henry's forces defeated them. The German army also easily defeated an invasion from the Danes. When Henry died in 936, he left behind him a peaceful Germany and a son, Otto, who claimed Charlemagne's old title of emperor, ruling over a united federation of German duchies.
04 May 2013
The Rule of Augustine
 |
| One Latin form of Augustine was "Austinus" |
Augustine did not, as St. Benedict did, set out to write a formal set of rules for an order. He did, however, leave a great deal of his written work behind. Three of these writings, taken together, are considered the Rule of St. Augustine.
The first is referred to as Letter 211, written in 423 to the nuns at Hippo (known to the modern world as Annaba, Algeria). It does not offer a list of specific actions to perform in their daily life; it was a more general letter about proper behavior during church services, embracing poverty and obedience, and the duties of the superior of the community. As the Bishop of Hippo, Augustine's letter was taken very seriously and read weekly to the nuns to remind them of their obligations.
 |
| Martin Luther was an Augustinian |
These Sermons and Letters were available to everyone over the centuries after Augustine. Benedict is said to have read and re-read Letter 211. It was not until 1256, however, that an actual Order of Saint Augustine was founded, when Pope Alexander IV issued a papal bull doing so.
03 May 2013
Dealing with Pagans
The Council of Constance (illustrated here) in 1414 has been mentioned before—or, at least, its outcomes. It was at this, the 16th ecumenical council recognized by the Roman Catholic Church, that Jan Hus and John Wycliffe were both condemned as heretics. There was more to the Council than that, however.
It also dealt with the Three Popes Controversy, forcing the ouster of antipopes John XXIII, Gregory XII, and Benedict XIII; they elected Pope Martin V.
One of the largest debates at the Council took place over the subject of how to deal with pagans. A few years earlier, the Teutonic Knights had fought against Poland and Lithuania; an uneasy and oft-broken peace existed between the players in that conflict, turning into another war in 1414. The Council of Constance was chosen as the place to decide the matter between the groups. The debate blossomed into a larger issue than where the borders should be: did the Teutonic Knights have a right to start the war in 1411? They had done so as a Crusade against the pagan inhabitants of those regions, intending to force them to convert to Christianity.
A doctor of canon law named Paulus Vladimir delivered an essay called Tractatus de potestate papa et imperatoris respect infidelium [Treatise on the power of the pope and emperor respecting infidels], in which he argued that a forced conversion was a violation of the right of free will granted by God. Free will was necessary for a true conversion. He claimed the Teutonic Knights could only wage a war if the enemy had done something to violate natural rights of Christians.
The opposing view said that the pope had every right to condemn pagans simply for being non-Christians. The loudest proponent of this view, John of Falkenburg, was condemned and imprisoned for his views, and for calling the Polish king a "mad dog."
The Council could not come to a conclusion, however. They established a diocese in Poland so that Christianity could be introduced more peacefully. The Polish-Teutonic wars resumed, on and off, for another century.
It also dealt with the Three Popes Controversy, forcing the ouster of antipopes John XXIII, Gregory XII, and Benedict XIII; they elected Pope Martin V.
One of the largest debates at the Council took place over the subject of how to deal with pagans. A few years earlier, the Teutonic Knights had fought against Poland and Lithuania; an uneasy and oft-broken peace existed between the players in that conflict, turning into another war in 1414. The Council of Constance was chosen as the place to decide the matter between the groups. The debate blossomed into a larger issue than where the borders should be: did the Teutonic Knights have a right to start the war in 1411? They had done so as a Crusade against the pagan inhabitants of those regions, intending to force them to convert to Christianity.
A doctor of canon law named Paulus Vladimir delivered an essay called Tractatus de potestate papa et imperatoris respect infidelium [Treatise on the power of the pope and emperor respecting infidels], in which he argued that a forced conversion was a violation of the right of free will granted by God. Free will was necessary for a true conversion. He claimed the Teutonic Knights could only wage a war if the enemy had done something to violate natural rights of Christians.
The opposing view said that the pope had every right to condemn pagans simply for being non-Christians. The loudest proponent of this view, John of Falkenburg, was condemned and imprisoned for his views, and for calling the Polish king a "mad dog."
The Council could not come to a conclusion, however. They established a diocese in Poland so that Christianity could be introduced more peacefully. The Polish-Teutonic wars resumed, on and off, for another century.
02 May 2013
Romsey Abbey: Its Ups & Downs
Romsey Abbey was, for a brief time, the home of Matilda of Scotland and her sister Mary. It is called "Romsey" because it was originally known as "Rum's Eg"—that is, the "area of Rum surrounded by marshes." It was founded by a granddaughter of Alfred the Great, Elflæda, in 907.
It went through some different stages, being refounded in 960 by King Edgar (943-975) as a Benedictine house under the control of the very pious (St.) Ethelflæda. The community thrived until it was sacked by Vikings in 993 and destroyed by fire. Rebuilt about 1000, it became a place to send the children of aristocrats for education (hence Matilda's time there).
A much larger building was erected in the original foundations around 1130 by Bishop Henry of Blois. That building still stands today. Between then and now, however, the Black Death wiped out all but 19 nuns of the religious community. The abbey never regained prominence, finally being suppressed (like so many others) in 1539 by Henry VIII (whose radical changes to the religious house of England was also mentioned here). The nuns were dispersed.
Even though the religious community was dissolved, however, the Abbey retained prominence in the town. Its church was being used as a parish church (St. Lawrence) by the larger community—an extra aisle had been added to the main structure so that townspeople had a place to attend services—and so Romsey did not suffer like many others: being left to fall into ruins or having its stone re-used in other building projects. Oddly, however, a few years later the townspeople purchased the building from the Crown and dismantled the extra aisle used as St. Lawrence, leaving the original Abbey church in which to worship.
In 1643, the English Civil War resulted in internal damage when soldiers tore up the seats and destroyed the organ. Many windows were damaged over the years and not replaced. The 19th century saw an attempt to restore the neglected structure, and now it has a thriving parish community.
It went through some different stages, being refounded in 960 by King Edgar (943-975) as a Benedictine house under the control of the very pious (St.) Ethelflæda. The community thrived until it was sacked by Vikings in 993 and destroyed by fire. Rebuilt about 1000, it became a place to send the children of aristocrats for education (hence Matilda's time there).
A much larger building was erected in the original foundations around 1130 by Bishop Henry of Blois. That building still stands today. Between then and now, however, the Black Death wiped out all but 19 nuns of the religious community. The abbey never regained prominence, finally being suppressed (like so many others) in 1539 by Henry VIII (whose radical changes to the religious house of England was also mentioned here). The nuns were dispersed.
Even though the religious community was dissolved, however, the Abbey retained prominence in the town. Its church was being used as a parish church (St. Lawrence) by the larger community—an extra aisle had been added to the main structure so that townspeople had a place to attend services—and so Romsey did not suffer like many others: being left to fall into ruins or having its stone re-used in other building projects. Oddly, however, a few years later the townspeople purchased the building from the Crown and dismantled the extra aisle used as St. Lawrence, leaving the original Abbey church in which to worship.
In 1643, the English Civil War resulted in internal damage when soldiers tore up the seats and destroyed the organ. Many windows were damaged over the years and not replaced. The 19th century saw an attempt to restore the neglected structure, and now it has a thriving parish community.
01 May 2013
To Marry a Nun
 |
| Seal of Queen Matilda |
Or was she?
Matilda was the daughter of Queen (later Saint) Margaret and Malcolm Canmore, King of Scotland (and the model for the Malcolm in Shakespeare's MacBeth). Her mother raised her with daily religious instruction and a ruthless attention to discipline: the steward had permission to beat any of her children if they exhibited bad manners.
At the age of six, Matilda (along with her three-year-old sister, Mary) was sent to Romsey Abbey in Hampshire, where their mother's sister was abbess. "Aunt Cristina" dressed the girls in the heavy black clothing of nuns and beat them regularly to remind them that they were sinful. Several years later, they were sent by their mother's instructions to Wilton Abbey in Wiltshire for further education, saving them from their aunt. Instruction included more than catechism: Matilda knew English, French and Latin, and was able to read St. Augustine and the Bible.
 |
| Romsey Abbey today |
Matilda herself testified that she was never meant to be a nun, that her parents only sent her to abbeys because they wished her to be educated, and that she hated the nun's life and tore off the veil whenever she was out of sight of Abbess Cristina. The council concluded that Matilda was never supposed to be a nun after all, and gave permission for the marriage.
30 April 2013
A Pain in the Ass
(I apologize if the title—or the topic—is too crude for some.)
The poor fellow to the right (the one half showing) is suffering from an anal fistula, described thusly:
The poor fellow to the right (the one half showing) is suffering from an anal fistula, described thusly:
... a small channel that can develop between the end of the bowel and the skin near the anus.
... can cause bleeding and discharge when passing stools - and can be painful. ...
In some cases, an anal fistula causes persistent drainage. In other cases, where the outside of the channel opening closes, the result may be recurrent anal abscesses. The only cure for an anal fistula is surgery. [WebMD]
Nowadays it is called a "pilonidal cyst." At the very least, inconvenient; in many cases, extremely painful, especially when sitting down.
At a time when many men spent long stretches of time bouncing on horseback, these fistula-in-ano (to give it the Latin phrase) were debilitating. Fortunately, soldiers of Edward III's time had a solution in the skill of John of Gaunt's favorite physician and surgeon.
John Arderne (1307-1392) left us very little information about his early life. It seems he was a surgeon in Nottinghamshire. During the Hundred Years War, he probably traveled with the army; his writing suggests a well-traveled man with wide experience of the world as well as medical practices.
He produced the definitive work on treating this particular medical problem. His writing describes the cause and the treatment, and describes the surgical instruments needed for his procedures. He also shows knowledge of Galen & Guy de Chauliac, Avicenna, and Dioscorides.
Arderne was ahead of his time in some ways. He advised opium to dull pain during surgery, and the code of conduct proper for a physician. In the matter of fees, he was fine with charging a rich patient whatever the traffic would bear, but felt that the poor should be treated for free. He was also a great believer in cleanliness, and in not fussing with a wound once treated, but allowing the healing process to proceed untampered with.
That is not to say that he was "modern." He also subscribed to the belief that parts of the body were aligned with astrological signs, and that the time of the year could influence the efficacy of surgery on parts of the body.
26 April 2013
The Beast of Provence
The "Beast of Provence" (also known as the "Giant of Provence" or "Bald Mountain") is actually Mont Ventoux [Mount Windy] in Provence. You have probably seen it on television: it is a major part of the Tour de France. It is made challenging not only because it is the highest mountain in the region, but also because of the high winds near the summit.
Winds blow over 50 miles per hour for the majority of the year, and speeds of 200 miles per hour have been recorded. The road over the mountain is often closed due to wind conditions.
The history of the Beast has always included an aura of foreboding, not just because of the wind. Its limestone peak—which can be seen from miles away—allows only sparse vegetation to grow, and so "Bald Mountain" appears to be barren and imposing.
Today is the anniversary of Petrarch's (1304-1374) ascent of Mont Ventoux in 1336. The writer claimed he was the first to do so since antiquity, even though his very own account mentioned meeting an old shepherd who had climbed it 50 years earlier. Petrarch has been cited as the first person to climb mountains for pleasure, incidentally creating "environmental writing" along the way by describing the surroundings and being inspired to introspection by them. (One of his musings at the peak is on his years of love for Laura.)
It is unlikely, however, that Petrarch was the first person to climb the mountain since antiquity—even besides the old shepherd. Jean Buridan (c.1300-1361) took a break from teaching at the University of Paris to climb the Beast, probably years before Petrarch. As for doing it "for pleasure": there are German writings from the 10th and 11th centuries about climbing mountains as a pleasant pastime.
23 April 2013
April 23rd
Let's see...so many to choose from.
The Feast Day of St. George, patron saint of England (who certainly did not exist)
Anniversary of Shakespeare's death (too late for "medieval")
Anniversary (supposedly) of Shakespeare's birth (too late, and really just wishful thinking)
Death of Ethelred the Unready
Ah. Here we are:
Founding of the Order of the Garter in 1348 by Edward III.
The story of the founding of the Order is well-known and unverified, told by Froissart, who loved court stories but wasn't present at the time (and was only a child). It tells us that the Countess of Salisbury lost her garter while dancing at a court ball, to the discourteous amusement of the guests. Edward III gallantly picked up the garter and handed it back to her, saying "Honi soi qui mal y pens."["Shame to him who thinks evil."] This, supposedly, inspired him to create a chivalrous order named for the Garter. The Countess of Salisbury in question might have referred to Joan of Kent, who later became his daughter-in-law when she married the Prince of Wales (Edward, "the Black Prince"). Otherwise, it was Joan's mother-in-law, Catherine Montacute, whose husband was the 1st Earl of Salisbury. Later rumors were that she was the focus of inappropriate affection from Edward.
Other sources claim that Richard Lionheart had his soldiers tie garters around their legs in some acknowledgement of St. George, and that Edward wished to evoke both Richard and George when founding the Order.
Whatever the case of its founding, it is the most exclusive and prestigious Order in England and Wales, limited to the king, the Prince of Wales, and 24 additional knights. The original list is a Who's Who of political power in mid-14th century England—although some of them had to be knighted in 1348 to be able to receive the honor of the Order. "Ladies of the Garter" were also appointed, though without the prestige accorded the Knights of the Garter. King Henry VII ended this practice, but King Edward VII named his wife a Lady of the Garter, as did King George V and King George VI.
Queen Elizabeth II is an ex-officio member of the Order.
The Feast Day of St. George, patron saint of England (who certainly did not exist)
Anniversary of Shakespeare's death (too late for "medieval")
Anniversary (supposedly) of Shakespeare's birth (too late, and really just wishful thinking)
Death of Ethelred the Unready
Ah. Here we are:
Founding of the Order of the Garter in 1348 by Edward III.
The story of the founding of the Order is well-known and unverified, told by Froissart, who loved court stories but wasn't present at the time (and was only a child). It tells us that the Countess of Salisbury lost her garter while dancing at a court ball, to the discourteous amusement of the guests. Edward III gallantly picked up the garter and handed it back to her, saying "Honi soi qui mal y pens."["Shame to him who thinks evil."] This, supposedly, inspired him to create a chivalrous order named for the Garter. The Countess of Salisbury in question might have referred to Joan of Kent, who later became his daughter-in-law when she married the Prince of Wales (Edward, "the Black Prince"). Otherwise, it was Joan's mother-in-law, Catherine Montacute, whose husband was the 1st Earl of Salisbury. Later rumors were that she was the focus of inappropriate affection from Edward.
Other sources claim that Richard Lionheart had his soldiers tie garters around their legs in some acknowledgement of St. George, and that Edward wished to evoke both Richard and George when founding the Order.
Whatever the case of its founding, it is the most exclusive and prestigious Order in England and Wales, limited to the king, the Prince of Wales, and 24 additional knights. The original list is a Who's Who of political power in mid-14th century England—although some of them had to be knighted in 1348 to be able to receive the honor of the Order. "Ladies of the Garter" were also appointed, though without the prestige accorded the Knights of the Garter. King Henry VII ended this practice, but King Edward VII named his wife a Lady of the Garter, as did King George V and King George VI.
Queen Elizabeth II is an ex-officio member of the Order.
22 April 2013
Medieval Chechnya
Recent events in Boston have underscored what Americans do not know about world geography. The news that the alleged bombers were Chechen, from Chechnya, led many to link them erroneously to Czechoslovakia. Chechnya, in the North Caucasus (north of Georgia, between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea), has a long and varied history.
The first time that the history of the area would overlap with topics dealt with by DailyMedieval is in the 13th and 14th centuries, when Mongols launched a prolonged effort to expand into Chechnya. At the time, however, it was not called "Chechnya" and was not Muslim; it was the region occupied by the Vainakh kingdom. The Vainakh were a branch of people who spoke one of the Nakh family of languages. The Nakh language is still spoken by Chechens, Ingush and Georgian Kist peoples.
Prior to the Mongol invasions, the region was influenced by Georgian Christian missionaries, although conversions were rare. They also traded with other areas cultures: Mesopotamian coins have been found, and a cache of 200 Arabian silver drahims from the 9th century. One of the effects of the Mongol invasions was the severing of easy communication with Georgia, after which Vainakh paganism re-asserted itself.
The Vainakh religion has similarities to Celtic beliefs, and some* think the Celtic Alans/Alauni might have come from the Vainakh region. Among the similarities that support a connection are veneration of trees, particularly the pine tree on the Winter Solstice, festivals at the time of Beltane and Halloween, and a wide range of gods.
Tamerlane (1336-1405) also led invasions into the region while attempting to restore the Mongol Empire of Genghis Khan. He devastated the North Caucasus. In the 15th century, while Russia began to encroach onto the territory, the local peoples converted to Sunni Islam in order to gain an ally in the Ottoman Empire and stave off Russia. There is a tradition that the word "Chechen" to refer to the inhabitants of the area comes from the village of Chechen-Aul where Russian forces were defeated in 1732. The term had been used in Russian sources 40 years earlier, however. It is likely that the name comes from Arabic sources and became common after the conversion to Islam: the term "Chechen" for these people appears in Arabic sources as far back as the 8th century.
*Jaimoukha, Amjad. The Chechens.
The first time that the history of the area would overlap with topics dealt with by DailyMedieval is in the 13th and 14th centuries, when Mongols launched a prolonged effort to expand into Chechnya. At the time, however, it was not called "Chechnya" and was not Muslim; it was the region occupied by the Vainakh kingdom. The Vainakh were a branch of people who spoke one of the Nakh family of languages. The Nakh language is still spoken by Chechens, Ingush and Georgian Kist peoples.
Prior to the Mongol invasions, the region was influenced by Georgian Christian missionaries, although conversions were rare. They also traded with other areas cultures: Mesopotamian coins have been found, and a cache of 200 Arabian silver drahims from the 9th century. One of the effects of the Mongol invasions was the severing of easy communication with Georgia, after which Vainakh paganism re-asserted itself.
The Vainakh religion has similarities to Celtic beliefs, and some* think the Celtic Alans/Alauni might have come from the Vainakh region. Among the similarities that support a connection are veneration of trees, particularly the pine tree on the Winter Solstice, festivals at the time of Beltane and Halloween, and a wide range of gods.
Tamerlane (1336-1405) also led invasions into the region while attempting to restore the Mongol Empire of Genghis Khan. He devastated the North Caucasus. In the 15th century, while Russia began to encroach onto the territory, the local peoples converted to Sunni Islam in order to gain an ally in the Ottoman Empire and stave off Russia. There is a tradition that the word "Chechen" to refer to the inhabitants of the area comes from the village of Chechen-Aul where Russian forces were defeated in 1732. The term had been used in Russian sources 40 years earlier, however. It is likely that the name comes from Arabic sources and became common after the conversion to Islam: the term "Chechen" for these people appears in Arabic sources as far back as the 8th century.
*Jaimoukha, Amjad. The Chechens.
19 April 2013
Movie Trivia
Every once in awhile, I decide to throw in bits and pieces that come my way but don't fit into a regular post. I did one here for the date of October 6th, and I gave an Update to cover some odds and ends I came across long after writing about certain subjects.
Since Becket has been on my mind (and on these pages) the past week, I cannot help thinking about how many people are probably familiar with him through the movie Becket, based on the play by Jean Anouilh. Made in 1964, it stars Richard Burton as Becket and Peter O'Toole as Henry II. The portrayal of Becket and his relationship with the king is inaccurate; Anouilh based it on a book he bought for his library whose green cover he thought would look good on his shelves. The book was not a true history, but Anouilh found that out after finishing the play, and altering his characters to reflect the truth would involve rewriting the entire play.
Perhaps it was the success of Becket that prompted the filming of A Man For All Seasons, based on the play by Robert Bolt of the same name, in which we see the tumultuous consequences suffered by (Saint) Sir Thomas More (Paul Scofield) when he refused to acknowledge King Henry VIII (Robert Shaw, probably better remembered to modern audiences as Captain Quint in Jaws) as the head of the new Church of England.
Peter O'Toole would play Henry II again in 1967, against Katharine Hepburn as Eleanor of Aquitaine, in The Lion in Winter. Like Becket, the movie was good, though the history was bad.
I've also mentioned The Anarchy as the backdrop for part of Theobald of Bec's career. The Anarchy is the era in which the Brother Cadfael mysteries of Ellis Peters take place.
I call Pope Celestine V "the pope who quit"; Dan Brown's Angels and Demons book and movie use him as an example of a murdered pope. (Dan Brown's books should not be used as history.)
Speaking of bad history and historical conspiracy theories, William of Gellone is a prominent figure in Holy Blood, Holy Grail by Baigent, Leigh, and Lincoln. Dan Brown's work shows the influence of this book.
...and that's enough trivia for another several months.
I've also mentioned The Anarchy as the backdrop for part of Theobald of Bec's career. The Anarchy is the era in which the Brother Cadfael mysteries of Ellis Peters take place.
I call Pope Celestine V "the pope who quit"; Dan Brown's Angels and Demons book and movie use him as an example of a murdered pope. (Dan Brown's books should not be used as history.)
Speaking of bad history and historical conspiracy theories, William of Gellone is a prominent figure in Holy Blood, Holy Grail by Baigent, Leigh, and Lincoln. Dan Brown's work shows the influence of this book.
...and that's enough trivia for another several months.
18 April 2013
Theobald of Bec
Since we brought up Canterbury yesterday, and arguably its most famous archbishop, let us take a look at his predecessor, who was very much at odds with the King of England for the same reasons, but hasn't made it into as many history books.
Theobald (c.1090-1161) was born in Normandy. He joined the abbey at Bec as a Benedictine and became its abbot in 1137. A year later, King Stephen of England appointed him the Archbishop of Canterbury. Theobald's relationship with the king was not ideal, especially when he clashed with the king's younger brother, Henry of Blois, who happened to be the Bishop of Winchester. Theobald was Henry's superior, but when your brother is the king, I suppose you tend to think you can get away with a little insubordination. Henry was appointed papal legate by Pope Celestine II, giving him some extra authority, but when Celestine died and Pope Innocent II (mentioned here) took the throne of Peter, Henry lost his position. Innocent did not like King Stephen, and wanted to appoint Theobald as his legate. This required Theobald to travel to meet the pope, which King Stephen forbade. Theobald went anyway.
Which brings us to the major issue between Theobald and King Stephen—and it's the same issue that created the greatest difficulties between Thomas Becket and King Henry II: who makes the decisions, the leader of the country or the leader of the church? The Archbishop was appointed/approved by the king, but did that give the king authority over everything the archbishop did in the future?
(For more on Stephen of Blois and his attitude toward his own right to authority, see how he took the throne in during The Anarchy, Parts One, Two, and Three, along with this.)
One of Theobald's acts that exacerbated this conflict between temporal and spiritual authority was a synod Theobald called in 1151. It comprised mostly the bishops of the land, but the king and his son and heir, Eustace, were invited. The synod made eight new statutes, including ones forbidding taxing church property, or seizing church property, or prosecuting clergy in the royal courts as opposed to church courts.
An even worse slap in Stephen's face came a year later, when Stephen wanted to crown Eustace as his heir.* Theobald refused to participate, claiming that to crown Eustace and legitimize Stephen's dynasty would be perpetuating a crime. (See the four links above, describing how Stephen claimed the throne for himself.)
The civil war ("The Anarchy"; see above) that came not long after the death of Eustace on the White Ship tore England apart for years, until the Treaty of Wallingford. Ironically, the negotiations that brought peace between Stephen and Henry of Anjou (later King Henry II) were managed by Theobald and his long-time enemy, Henry of Blois. When Stephen died in October 1154, Theobald attended him on his deathbed; Stephen named Theobald regent until Henry could take up the reins of power. Although the two had feuded, there is evidence of mutual respect that allowed them ultimately to work together.
Theobald had the same relationship with Henry II, fighting over authority to try clergy in ecclesiastical courts rather than secular courts, and protecting church property from royal interference. Theobald helped his protégé, Thomas Becket, become chancellor. Becket seems to have become very close to the king, so close that the king was glad to make him Archbishop of Canterbury upon Theobald's death. That arrangement, however, if it was intended to make Henry's dealing with the church any easier than under Theobald, was surely a disappointment to the king. Becket proved to be as protective of the church and clergy as Theobald was. (But then, everyone knows how that turned out.)
*The Capetian Dynasty followed the practice of crowning the heir while his predecessor was still alive, previously posted about here.
17 April 2013
Chaucer Performs
Whan that Aprille with his shoures soote
The droghte of Marche hath perced to the roote
DailyMedieval doesn't usually talk about topics that everyone knows about (King Arthur, Geoffrey Chaucer, jousting and castles, etc.), because it tries to pull back the curtain on all the other interesting people and places and tidbits of knowledge that do not get any exposure in textbooks or modern popular culture. (Not that I don't have a strong feelings about Chaucer, as the book link in the upper-right corner of this website tells you.)
 |
| From the Ellesmere manuscript |
Spring was the time when folk "longed to go on pilgrimages" because they had been cooped up indoors all winter and the roads were finally becoming navigable.
Canterbury was a common goal for pilgrimages because it held the shrine of Thomas Becket, Archbishop of Canterbury from 1162-1170, who was killed during the reign of Henry II by four knights who were acting either on behalf of the King or were removing the king's rival on their own in order to curry favor. He was universally loved by the population of England, and was declared a martyr by Pope Alexander III in 1173.
While we're on the subject, let's make something clear about The Canterbury Tales: it is not a complete work. In the collection, the proposal for the pilgrims is that they would each tell two tales heading to Canterbury and two tales coming back, after which their Host would judge the best tale. Chaucer's intent was possibly to top Boccaccio's Decameron with its ten tales each day for ten days. We have barely over 30 tales (and some of them fragmentary), a far cry from the 120 we could expect if he completed the work.
16 April 2013
The Map You Walk On
Madaba, a town east of the Dead Sea, suffered from a devastating earthquake in 746 and was left to become wilderness. Centuries later, Madaba began slowly to be restored as a habitable city. In 1884, while the ancient ruins of a church were being cleared to make way for a new Greek Orthodox church, workers discovered a mosaic on the floor.
The Madaba Mosaic Map is considered a reliable source of data on Byzantine-era Jerusalem because of the detail with which it is constructed. Known old structures such as the Damascus Gate, the Tower of David, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre and others are depicted with enough detail to distinguish them from simple symbolic images. The detail even allows scholars to date the map: Jerusalem shows the Nea Church, which was built and in use by 542, but does not show any changes or structures built after 570. In fact, the Nea Church was only able to be discovered by archaeologists when they used the Madaba Mosaic as their cue for where to dig! Furthermore, the exact location of the ancient Jewish city of Askalon/Ashkelon was uncertain until the Madaba Mosaic showed where it was on the coast.
The floor mosaic faced east, toward the altar. Therefore, when one was facing the altar, one was facing in the proper direction to orient the map with the real world. All the inscriptions are in Greek. The map extends from Lebanon in the north to the Nile Delta, and the Mediterranean to the Eastern Desert. The original dimensions were 21 meters by 7 meters and would have required over 2,000,000 individual tiles, but damage over the years has reduced it by about a third, to 16x5 meters. We do know that some of it was damaged deliberately in the 8th century when Muslim rulers had depictions of people removed. Now carefully preserved, it can be seen in the Greek Orthodox Church of St George.
The Madaba Mosaic Map is considered a reliable source of data on Byzantine-era Jerusalem because of the detail with which it is constructed. Known old structures such as the Damascus Gate, the Tower of David, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre and others are depicted with enough detail to distinguish them from simple symbolic images. The detail even allows scholars to date the map: Jerusalem shows the Nea Church, which was built and in use by 542, but does not show any changes or structures built after 570. In fact, the Nea Church was only able to be discovered by archaeologists when they used the Madaba Mosaic as their cue for where to dig! Furthermore, the exact location of the ancient Jewish city of Askalon/Ashkelon was uncertain until the Madaba Mosaic showed where it was on the coast.
The floor mosaic faced east, toward the altar. Therefore, when one was facing the altar, one was facing in the proper direction to orient the map with the real world. All the inscriptions are in Greek. The map extends from Lebanon in the north to the Nile Delta, and the Mediterranean to the Eastern Desert. The original dimensions were 21 meters by 7 meters and would have required over 2,000,000 individual tiles, but damage over the years has reduced it by about a third, to 16x5 meters. We do know that some of it was damaged deliberately in the 8th century when Muslim rulers had depictions of people removed. Now carefully preserved, it can be seen in the Greek Orthodox Church of St George.
14 April 2013
The Ethiopian Connection
In the Middle Ages, the evidence suggests that Ethiopia was a Christian nation surrounded by hostile Muslim territories. Medieval manuscripts explain that there was a Solomonic dynasty in Ethiopia—that is, the heirs of King Solomon, descended from the son born to the Queen of Sheba. Unprovable, but it would explain the Christian presence in that part of the world. In fact, "Dawit I" is what he is called in the West; Ethiopian sources call him "Dawit II," because they consider the first "Dawit" to be King David.
One of the members of the heirs of Solomon was Dawit I (1382-1413). There are stories that Dawit led armies against his Muslim neighbors to the east, and that he also advanced against the emir that held Egypt at the time, until the emir asked the Patriarch of Alexandria to tell Dawit to cease in order to preserve the peace in the kingdom.
There is also reason to believe that he was in communication with Europe, making a request to Venice to send him artisans for the beautification of his realm. Documentary evidence exists that this request reached Venice in June 1402, and that 5 artisans did leave for Ethiopia.
We don't know if they ever arrived, but we can turn to circumstantial evidence. The Portugese missionary and explorer, Francisco Álvares (c.1465-c.1540), claims to have seen a Venetian chalice during his six years in Ethiopia. Also, an unsigned manuscript exists that documents a trip from Venice to Rhodes, Cyprus, Jerusalem, Cairo, and finally to the court of Prester John at Shewa, a region in Ethiopia that has Addis Ababa (Ethiopia's modern capital) at its center. (Prester John was often said to have his kingdom "in India"; for most Europeans, however, geography outside of Europe was a pretty vague topic. You can learn more about Prester John here and here). This itinerary shows an unambiguous knowledge of the stages of a journey from Venice to Ethiopia, suggesting that perhaps the legend of Dawit's interest in European artwork was based on truth.
Alas, Dawit died young, kicked in the head by a horse. He is interred at a monastery on Daga Island in Lake Tana, the source of the Blue Nile, along with other members of his dynasty.
One of the members of the heirs of Solomon was Dawit I (1382-1413). There are stories that Dawit led armies against his Muslim neighbors to the east, and that he also advanced against the emir that held Egypt at the time, until the emir asked the Patriarch of Alexandria to tell Dawit to cease in order to preserve the peace in the kingdom.
There is also reason to believe that he was in communication with Europe, making a request to Venice to send him artisans for the beautification of his realm. Documentary evidence exists that this request reached Venice in June 1402, and that 5 artisans did leave for Ethiopia.
We don't know if they ever arrived, but we can turn to circumstantial evidence. The Portugese missionary and explorer, Francisco Álvares (c.1465-c.1540), claims to have seen a Venetian chalice during his six years in Ethiopia. Also, an unsigned manuscript exists that documents a trip from Venice to Rhodes, Cyprus, Jerusalem, Cairo, and finally to the court of Prester John at Shewa, a region in Ethiopia that has Addis Ababa (Ethiopia's modern capital) at its center. (Prester John was often said to have his kingdom "in India"; for most Europeans, however, geography outside of Europe was a pretty vague topic. You can learn more about Prester John here and here). This itinerary shows an unambiguous knowledge of the stages of a journey from Venice to Ethiopia, suggesting that perhaps the legend of Dawit's interest in European artwork was based on truth.
Alas, Dawit died young, kicked in the head by a horse. He is interred at a monastery on Daga Island in Lake Tana, the source of the Blue Nile, along with other members of his dynasty.
08 April 2013
The Flying Monk
Did a monk of the 11th century accomplish the first manned flight? There is reason to believe so.
In the Gesta Regum Anglorum [Deeds of the English Kings] of William of Malmesbury, we read of a monk named Eilmer in Malmesbury Abbey who launched himself from the Abbey's tower with a set of home-made wings. According to the story, he glided more than a furlong (a furlong is 220 yards, or just over 200 meters). Then, suddenly realizing how precarious his position was, he panicked, lost control, and crashed, breaking both legs. He had extreme difficulty walking for the rest of his life.
How likely is this story to be true? Let's first consider what we might call "incidental" evidence. William is not just reporting a legend: although he lived after Eilmer, he was in the same Abbey, and very likely got the story from elders who knew Eilmer and had witnessed the experiment first-hand.
William also records a curious detail: that Eilmer ever after claimed his failure was due to not constructing a tail for his device. This suggests that Eilmer really did study birds in flight, and realized that a tail is also important to steer and brake for landing. Unfortunately for the history of manned flight, the abbot forbade him or anyone from repeating the crippling experience.
But was such a flight possible? Several historians have weighed in, and even the United States Air Force is willing to accept it. The conditions that make it believable are as follows:
The Abbey was situated at a cliff edge over the Avon River that would have created strong updrafts. Eilmer would have seen how jackdaws use the strong updraft to glide and soar without the need to flap. The tower would have been about 80 feet high, giving him additional altitude for catching an updraft. If Eilmer were a small man, calculations suggest that a light and strong frame of willow or ash, covered with parchment or light cloth, would only need an area of 100 square feet to support his weight. William says the wings were attached to Eilmer's hands as well as feet—this supports the notion that they covered a larger area than just wings attached to arms.
 Local legend says his landing spot is an area now called "Oliver's Lane." (Ralph Higden's Polychronicon—mentioned here—erroneously referred to Eilmer as Oliver, and the name stuck.) Given the constant wind conditions and the distance he is supposed to have flown, Oliver's Lane is precisely where modern calculations based on wind currents place his likely landing spot. The gliding flight would have lasted about 15 seconds.
Local legend says his landing spot is an area now called "Oliver's Lane." (Ralph Higden's Polychronicon—mentioned here—erroneously referred to Eilmer as Oliver, and the name stuck.) Given the constant wind conditions and the distance he is supposed to have flown, Oliver's Lane is precisely where modern calculations based on wind currents place his likely landing spot. The gliding flight would have lasted about 15 seconds.
He lived a long time afterward, becoming known for scholarship. His writing on astronomy existed and was well-known into the 16th century, but has been lost since. Also lost to history is the tavern "The Flying Monk" in Malmesbury, which has since been replaced by a shopping center.
In the Gesta Regum Anglorum [Deeds of the English Kings] of William of Malmesbury, we read of a monk named Eilmer in Malmesbury Abbey who launched himself from the Abbey's tower with a set of home-made wings. According to the story, he glided more than a furlong (a furlong is 220 yards, or just over 200 meters). Then, suddenly realizing how precarious his position was, he panicked, lost control, and crashed, breaking both legs. He had extreme difficulty walking for the rest of his life.
How likely is this story to be true? Let's first consider what we might call "incidental" evidence. William is not just reporting a legend: although he lived after Eilmer, he was in the same Abbey, and very likely got the story from elders who knew Eilmer and had witnessed the experiment first-hand.
William also records a curious detail: that Eilmer ever after claimed his failure was due to not constructing a tail for his device. This suggests that Eilmer really did study birds in flight, and realized that a tail is also important to steer and brake for landing. Unfortunately for the history of manned flight, the abbot forbade him or anyone from repeating the crippling experience.
But was such a flight possible? Several historians have weighed in, and even the United States Air Force is willing to accept it. The conditions that make it believable are as follows:
The Abbey was situated at a cliff edge over the Avon River that would have created strong updrafts. Eilmer would have seen how jackdaws use the strong updraft to glide and soar without the need to flap. The tower would have been about 80 feet high, giving him additional altitude for catching an updraft. If Eilmer were a small man, calculations suggest that a light and strong frame of willow or ash, covered with parchment or light cloth, would only need an area of 100 square feet to support his weight. William says the wings were attached to Eilmer's hands as well as feet—this supports the notion that they covered a larger area than just wings attached to arms.
 Local legend says his landing spot is an area now called "Oliver's Lane." (Ralph Higden's Polychronicon—mentioned here—erroneously referred to Eilmer as Oliver, and the name stuck.) Given the constant wind conditions and the distance he is supposed to have flown, Oliver's Lane is precisely where modern calculations based on wind currents place his likely landing spot. The gliding flight would have lasted about 15 seconds.
Local legend says his landing spot is an area now called "Oliver's Lane." (Ralph Higden's Polychronicon—mentioned here—erroneously referred to Eilmer as Oliver, and the name stuck.) Given the constant wind conditions and the distance he is supposed to have flown, Oliver's Lane is precisely where modern calculations based on wind currents place his likely landing spot. The gliding flight would have lasted about 15 seconds.He lived a long time afterward, becoming known for scholarship. His writing on astronomy existed and was well-known into the 16th century, but has been lost since. Also lost to history is the tavern "The Flying Monk" in Malmesbury, which has since been replaced by a shopping center.
31 March 2013
Quartodecimans & Easter
This blog has touched on the debate over the date of Easter in the past, but the truth is that the early Church went through different phases before settling on the date of Easter.
Because the Last Supper was a seder, commemorating Passover, early celebrations of Easter coincided with that date. Passover took place on the 14th of the month. The early Church historian Eusebius tells us that the dioceses of Asia at the time of Pope Victor (pope from 189-199) celebrated Easter on the 14th day of the moon, regardless of the day of the week on which it fell.
This bothered some ecclesiastics and Christian scholars. Synods were held (Eusebius says) that agreed and decreed that the Easter celebration should be held on the Lord's Day, a Sunday. Some, however, refused to give up the tradition of celebrating on the 14th. They were called Quartodecimans [fourteenth-ers]. St. Polycarp (69-155), for example, came to Rome to discuss his preference for the date that he believed had been established by St. John the Apostle; he refused the command of Pope Anicetus (pope c.153-168) to change to Sunday.
Quartodecimans were tolerated for awhile, by popes like Anicetus at least. Pope Victor excommunicated the Asiatic dioceses, an action that got him criticism for unnecessary harshness from St. Irenæus.
Agreeing that Easter should be celebrated on a Sunday did not settle any debate; which Sunday was crucial. The Council of Nicaea (already mentioned several times in DM) tackled this issue. Syrian Christians always celebrated Easter on the Sunday following the 14th of the month, but other Christian dioceses calculated the date in their own ways. Antioch, for instance, based their date on the local Jewish observances, but had let slide a guideline that the 14th should be the month after the vernal equinox. Alexandria, however, demanded Easter Sunday be after the equinox—March 21st at the time.
Most native English speakers, if they know about the controversy of the Easter date debate, have heard of the Synod of Whitby in 664, at which Roman Christianity and Celtic/Irish Christianity fought it out over topics such as the date of Easter and the style of monastic tonsures. Whitby established for the English-speaking world that Easter would fall on the first Sunday after the first full moon (the 14th of the lunar month) after the vernal equinox. If the full moon is a Sunday, Easter takes place on the following Sunday. Easter can be as early as March 22 or as late as April 25.
The Eastern Orthodox Church calculates differently. They had been using March 21st as their starting point, but followed a guideline that prevented Easter from ever falling on or preceding the same day as Passover. Orthodox Easter can fall between April 5 and May 8. In the 21st century, the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches tried to reconcile their different dates using more recent astronomical data for their calculations. They still calculate in different ways, but there is greater chance that the dates will coincide, such as in 2001 when April 15th was Easter for both Churches.
There. That was easy.
Because the Last Supper was a seder, commemorating Passover, early celebrations of Easter coincided with that date. Passover took place on the 14th of the month. The early Church historian Eusebius tells us that the dioceses of Asia at the time of Pope Victor (pope from 189-199) celebrated Easter on the 14th day of the moon, regardless of the day of the week on which it fell.
This bothered some ecclesiastics and Christian scholars. Synods were held (Eusebius says) that agreed and decreed that the Easter celebration should be held on the Lord's Day, a Sunday. Some, however, refused to give up the tradition of celebrating on the 14th. They were called Quartodecimans [fourteenth-ers]. St. Polycarp (69-155), for example, came to Rome to discuss his preference for the date that he believed had been established by St. John the Apostle; he refused the command of Pope Anicetus (pope c.153-168) to change to Sunday.
Quartodecimans were tolerated for awhile, by popes like Anicetus at least. Pope Victor excommunicated the Asiatic dioceses, an action that got him criticism for unnecessary harshness from St. Irenæus.
Agreeing that Easter should be celebrated on a Sunday did not settle any debate; which Sunday was crucial. The Council of Nicaea (already mentioned several times in DM) tackled this issue. Syrian Christians always celebrated Easter on the Sunday following the 14th of the month, but other Christian dioceses calculated the date in their own ways. Antioch, for instance, based their date on the local Jewish observances, but had let slide a guideline that the 14th should be the month after the vernal equinox. Alexandria, however, demanded Easter Sunday be after the equinox—March 21st at the time.
Most native English speakers, if they know about the controversy of the Easter date debate, have heard of the Synod of Whitby in 664, at which Roman Christianity and Celtic/Irish Christianity fought it out over topics such as the date of Easter and the style of monastic tonsures. Whitby established for the English-speaking world that Easter would fall on the first Sunday after the first full moon (the 14th of the lunar month) after the vernal equinox. If the full moon is a Sunday, Easter takes place on the following Sunday. Easter can be as early as March 22 or as late as April 25.
The Eastern Orthodox Church calculates differently. They had been using March 21st as their starting point, but followed a guideline that prevented Easter from ever falling on or preceding the same day as Passover. Orthodox Easter can fall between April 5 and May 8. In the 21st century, the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches tried to reconcile their different dates using more recent astronomical data for their calculations. They still calculate in different ways, but there is greater chance that the dates will coincide, such as in 2001 when April 15th was Easter for both Churches.
There. That was easy.
30 March 2013
Anti-kings? Really?
Rudolph of Swabia was referred to as an anti-king after he was defeated by Henry IV in 1080. Anti-popes are a common concept in history, but were there enough anti-kings to justify a label? Can't we just call him a usurper?
There were actually quite a few anti-kings in the Middle Ages. One of the earliest was Duke Arnulf "The Bad" of Bavaria, who spent 919-921 claiming he was the alternative to King Henry "The Fowler" who was the first king of the Ottonian dynasty in Germany. After Henry defeated Arnulf in battle, he allowed Arnulf to keep the title of Duke of Bavaria so long as he renounced forever his claim to the German throne. Arnulf wised up, and did not create any more trouble, dying peacefully in 937.
Rudolf of Swabia was an anti-king who has already been referenced when discussing Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV and his conflict with Pope Gregory VII. When Henry was out of favor, German aristocrats decided to elect an alternate, Rudolf, who lasted from 1077-1080. After he died in battle, Hermann of Luxembourg (also called "of Salm") took a chance. He lasted longer than Rudolf, from 1081-1088, but had to flee to Denmark in 1085. He returned in an alliance with Duke Welf of Bavaria, Rudolph's successor, but soon tired of the constant struggle (and being a pawn of the pope and German lords) and retired to his home. He was not heard of after 1088; we assume that was the year of Hermann's death.
The Germans either had a difficult time accepting their anointed rulers, or they just liked creating conflict. Several Holy Roman Emperors had to deal with anti-king challenges, right up until the mid-14th century!
There were actually quite a few anti-kings in the Middle Ages. One of the earliest was Duke Arnulf "The Bad" of Bavaria, who spent 919-921 claiming he was the alternative to King Henry "The Fowler" who was the first king of the Ottonian dynasty in Germany. After Henry defeated Arnulf in battle, he allowed Arnulf to keep the title of Duke of Bavaria so long as he renounced forever his claim to the German throne. Arnulf wised up, and did not create any more trouble, dying peacefully in 937.
Rudolf of Swabia was an anti-king who has already been referenced when discussing Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV and his conflict with Pope Gregory VII. When Henry was out of favor, German aristocrats decided to elect an alternate, Rudolf, who lasted from 1077-1080. After he died in battle, Hermann of Luxembourg (also called "of Salm") took a chance. He lasted longer than Rudolf, from 1081-1088, but had to flee to Denmark in 1085. He returned in an alliance with Duke Welf of Bavaria, Rudolph's successor, but soon tired of the constant struggle (and being a pawn of the pope and German lords) and retired to his home. He was not heard of after 1088; we assume that was the year of Hermann's death.
The Germans either had a difficult time accepting their anointed rulers, or they just liked creating conflict. Several Holy Roman Emperors had to deal with anti-king challenges, right up until the mid-14th century!
27 March 2013
Canon Law and Muslims
Today picks up from the previous post.
Although canon law did not apply to non-Christian populations, that attitude changed when Europe came into greater contact with Muslims. The reason is explained by James Brundage:
In the 13th century, Pope Innocent IV (c.1195-1254; pope from 1243 until his death) declared that ownership of property was a human right, as part of the natural law established by God. He also declared, however, that although non-Christians may not be part of Christ's church, they were still part of Christ's flock, and therefore they should fall under the rule of Christ's vicar on Earth. (Innocent even sent a message to Güyük Khan, "Emperor of the Tartars" (c.1206-1248), to tell the Mongol ruler to convert to Christianity and stop fighting Europeans. The response from the Khan was that European rulers should submit to his rule.)
This view of the popes prevailed, reaching a peak in 1302 with Boniface VIII's papal bull, Unam Sanctam. For the next several centuries, Christian rulers had the license they needed to attack non-Christians and take their lands.
Although canon law did not apply to non-Christian populations, that attitude changed when Europe came into greater contact with Muslims. The reason is explained by James Brundage:
European Jewry had furnished the model upon which early canonists had formed their views about the legal relationship between non-Christians and canon law. Jewish populations, however, tended to be relatively small, stable (save when one ruler or another decided to expel them from his territories), and peaceful. They certainly posed no military threat to Christian rulers and only an occasional fanatic could seriously maintain that they menaced the Christian religious establishment.This interaction with the Muslim world caused canonists to re-examine the self-imposed limits of canon law and its application to non-Christians, especially when it came to whether it was proper for Christians to conquer and take Muslim territory. This may seem an odd concern to the modern reader, but remember that this was a time when ownership of property was not open to everyone. If Muslims fell into a category that was not allowed property—such as slaves or minors—then taking their lands was not an issue.
Muslims in the Mediterranean basin and pagans along Latin Christendom's eastern frontiers, however, were an altogether different matter. Many Christians considered them a serious threat to Christianity's goal of converting the world... . [Medieval Canon Law, p.163]
In the 13th century, Pope Innocent IV (c.1195-1254; pope from 1243 until his death) declared that ownership of property was a human right, as part of the natural law established by God. He also declared, however, that although non-Christians may not be part of Christ's church, they were still part of Christ's flock, and therefore they should fall under the rule of Christ's vicar on Earth. (Innocent even sent a message to Güyük Khan, "Emperor of the Tartars" (c.1206-1248), to tell the Mongol ruler to convert to Christianity and stop fighting Europeans. The response from the Khan was that European rulers should submit to his rule.)
This view of the popes prevailed, reaching a peak in 1302 with Boniface VIII's papal bull, Unam Sanctam. For the next several centuries, Christian rulers had the license they needed to attack non-Christians and take their lands.
25 March 2013
The Limits of Canon Law
Since I've been looking into canon law lately (here and here), I thought I would share an interesting facet of Medieval era canon law: its self-imposed limits.
Although canon law borrowed a great deal from the jurists and civil law decisions of the Classical Era, it was grounded in church teachings. Therefore, from early jurists up until at least 1200, it was agreed that canon law did not apply to non-Christians. The rules of consanguinity adhered to by the church, for instance, forbidding the marriage of those who were related too closely by blood or legal ties (such as in-laws), did not apply to Jews or pagans. Nor was it legal for Jews or pagans to be made to tithe or be baptized against their will.
Of course, Christianity's goal was to spread the Gospel and convert the world, so it would be only a matter of time (it was thought) before canon law would apply to everyone. (The second post ever on DailyMedieval was about the Domus Conversorum, established in 1232 in England by Henry III to provide a home and daily stipend for Jews who wished to convert to Christianity, making their decision an easy one.)
Christianity ran into an unexpected obstacle to its ultimate goal, however, especially during the era of the Crusades. Whereas Jews were found in small and non-violent communities, Muslims were far more numerous and warlike; moreover, they were on their own mission to convert the world. This led—outside of the Crusades themselves—to border skirmishes where newly acquired Middle East Christian territories brushed up against Muslim lands.
The debate that followed will be looked at in the next post.
Although canon law borrowed a great deal from the jurists and civil law decisions of the Classical Era, it was grounded in church teachings. Therefore, from early jurists up until at least 1200, it was agreed that canon law did not apply to non-Christians. The rules of consanguinity adhered to by the church, for instance, forbidding the marriage of those who were related too closely by blood or legal ties (such as in-laws), did not apply to Jews or pagans. Nor was it legal for Jews or pagans to be made to tithe or be baptized against their will.
Of course, Christianity's goal was to spread the Gospel and convert the world, so it would be only a matter of time (it was thought) before canon law would apply to everyone. (The second post ever on DailyMedieval was about the Domus Conversorum, established in 1232 in England by Henry III to provide a home and daily stipend for Jews who wished to convert to Christianity, making their decision an easy one.)
Christianity ran into an unexpected obstacle to its ultimate goal, however, especially during the era of the Crusades. Whereas Jews were found in small and non-violent communities, Muslims were far more numerous and warlike; moreover, they were on their own mission to convert the world. This led—outside of the Crusades themselves—to border skirmishes where newly acquired Middle East Christian territories brushed up against Muslim lands.
The debate that followed will be looked at in the next post.
23 March 2013
Ignorance of the Law
Ignorantia juris neminem excusat.
Ignorance of the law excuses no one.
Can ignorance of the law ever be an excuse?
The Middle Ages deliberated over this topic, ultimately drawing a distinction between two classes of people: those who had no excuse not to know the law, and those who did have an excuse for their ignorance. Canon law wanted to be strict and definitive, but it recognized that there were segments of society that could not be held completely responsible for their actions.
For whom was ignorance of the law an excuse? Actually, several groups were considered exempt from presumption of knowledge of the law:
...minors, madmen, soldiers, and, in most circumstances, women were commonly believed to lack the capacity (in the case of minors and the insane) or the opportunity (in the case of soldiers and women) to know and understand the law. [Medieval Canon Law, James Brundage, p.161]Much of medieval canon law came from Roman sources such as the Digestum Justiniani (the Digest of Justinian*) in 503. It assembled 50 books covering many topics by multiple jurists. In the Digestum, one classical jurist, Paul, draws a distinction between ignorance of the law and ignorance of fact. Although the legal system may not be able to presume that everyone knows the actual law, it must presume that everyone knows the fundamental factual difference between a good act and a bad act in their community. Otherwise, profession of one's ignorance becomes a universal excuse, and only those who are lawyers, judges, or politicians who actually make the laws would ever be able to be convicted.
Paul is also the jurist who created the basis for presumption of innocence when he wrote Ei incumbit probatio qui dicit, non qui negat. ("Proof is incumbent on him who asserts, not him who denies.") Although the accused could not avoid punishment by simply saying "I didn't know," at least he wasn't convicted based simply on another's say-so.**
*This was Emperor Justinian I (c.482-565), whose reign straddled the Classical and Medieval eras. The Digestum is not to be confused with the Corpus Juris Civilis (Body of Civil Law), the much larger compendium (sometime called the Code of Justinian) that was assembled later in his reign, of which the Digestum was only a part.
**The phrase "Innocent until proven guilty" was coined by the English lawyer Sir William Garrow in the early 19th century.
20 March 2013
It's My Day Off...Again
There were 52 days of the year that no one should have to labor: Sundays. For the same reason that Sundays were taken off—everyone should be free to attend Mass—there were about 40 days in the calendar that were likewise taken off because they were saints feast days or other Holy Days (Annunciation, Christmas, et cetera).
Furthermore, there were sometimes local saints in the area—not found in the official liturgical calendar established by the 12th century—whose celebrations workers were obliged to observe. These could add 20-30 additional days off to a worker. All in all, a potential 120 days—one-third of the year—could be spent in "enforced leisure." That leisure often included feasts and dances in the community. In a world without the forms of entertainment we are used to now, communal feasts and other social gatherings could be the highlights of the season.
This was not necessarily a good thing for the laborer or the employer. If he were paid by the day, he lost a lot of wages on the days when he was not supposed to work. If an employer paid by the month or the quarter, there were several days when he got no work out of his employees although they were being paid!
[For more, see Medieval Canon Law by James A. Brundage, ©1995 by Longman Group Limited]
06 March 2013
When Poets Collide?
Guillaume de Machaut (c.1300-1377) was a classical composer and poet—in fact, one of the last poets who also composed music—and a part of the ars nova ["new technique"] movement which embraced polyphony. His name suggests that he was born in Machault, east of Rheims in France, but it is clear that he spent most of his life in Rheims. Unlike many non-royal figures of his age, his popularity has ensured that we possess a remarkable amount of biographical information about him.
As a young man, he was a secretary to the ing of Bohemia, John I. He was named a canon of Verdun, then Arras, then Rheims; by 1340 he had given up the other positions and was a canon of Rheims only. As a canon, attached to the cathedral in Rheims and living without private wealth, he could devote himself to composing poetry and music. In all, we have about 400 pieces in various forms.
He lost his first patron, King John of Bohemia, when John died at the Battle of Crécy in 1346 during the Hundred Years War. Machaut found support from John's daughter. When she died during the Black Death, he found support from her sons, Jean de Berry and CharlesV, Duke of Normandy.
In the next phase of the Hundred Years War, Geoffrey Chaucer (likely still a teenager at the time) was in the retinue of Prince Lionel as a valet. During the siege of Rheims in early 1360, Rheims rallied and captured the besiegers. Chaucer was taken prisoner. This would not have involved being thrown in dungeons and experiencing deprivation. The practice at the time was to capture as many high-ranking opponents as possible in order to gain money from ransoms. (Chaucer was ransomed for £16 in March.) The English would have likely experienced a mild form of "house arrest" which would have allowed them a certain amount of freedom. Chaucer would have had ample opportunity to visit Machaut.
Did he? We cannot be sure. Chaucer's poetry rarely offers attribution for his influences, but he was certainly intimately familiar with Machaut's work. Scholars have found numerous influences in Chaucer's writing. Chaucer scholar James I. Wimsatt has referred to "Guillaume de Machaut, who among fourteenth-century French poets exerted by far the most important influence on Chaucer."[link] Even long before he himself began writing, he was in a court that valued and supported the arts and poetry. Machaut was enormously popular in his own lifetime, and it seems inconceivable that Machaut would not have been sought out by several of the English who would have appreciated his reputation.
For a sample of his musical composition:
05 March 2013
Queenshithe
 |
| Plaque in Queenhithe. |
The site is much older, however. As mentioned, it was no doubt established in Roman times—excavations have found remains of Roman baths in the area. When King Alfred the Great (849-899) "revived" the City of London around 886. Alfred made a gift of it to his brother-in-law Ethelred, and for a time it was called Ædereshyd, or "Ethelred's Dock."
It was an important landing place for ships bringing grain into the city. The nearby Bread Street has existed under that name at least as far back as the Agas Map. Also, Skinners Lane a block away attests to the import of furs, particularly rabbit skins.
It was designated a Scheduled Ancient Monument in 1973, particularly as it is the only surviving site of a once-Saxon harbor. It is therefore protected from random alterations by construction. Its use as a port, however, has fallen off because of its position upriver from London Bridge, preventing large modern ships from reaching it.
03 March 2013
Sir Richard Stury
 |
| King Edward and his knights counting their dead after the Battle of Crécy, Hundred Years War |
He was a chamber knight and a councilor to Edward III. He was also, like many of his fellow chamber knights, a lover of poetry. His will included an expensive copy of the Romance of the Rose.
He and Chaucer were well-acquainted. Their paths would have crossed frequently in London, and they were put together on an embassy in 1377 and a commission in 1390 to look into repairing the dikes and drains of the Thames.
Stury had a reputation for being a Lollard, a follower of the teachings of John Wycliffe. The popularity of this stance waxed and waned over the years, sometimes putting him in opposition to powerful forces in society.
03 February 2013
Banking Collapse of the 1340s
 |
| Chapels of the Bardi & Peruzzi families in Santa Croce, Florence |
Florence was the headquarters for some powerful families in the Middle Ages who used their wealth and business acumen (and the stability of the Florentine gold florin) to create the first international banking corporations. Two of the biggest, run by the Bardi and Peruzzi families, collapsed in 1346 and 1343, respectively. The excuse for the collapse is often given as Edward III of England's default on loans he took to pay for expenses during the Hundred Years War. Estimates put Edward's debts at 900,000 florins to the Bardi and 600,000 to the Peruzzi--an enormous sum in any age.
More recent assessments of the situation, however, spread the blame. Edward's expenses were incurred earlier, and the two banks survived for some years afterward. Also, a third bank, the Acciaiuoli, failed in 1343 without having loaned any money to England. Various Florentine banks also loaned money to finance a war against Castracane of Lucca, and to put down a peasant revolt in Flanders. Also, an uprising in September 1343 in Florence created vast property damage that would have affected the banks (according to the 16th century historian Giovanni Villani).
It is impossible to understand every aspect of the collapse of the 1340s, especially since records such as we expect modern companies to maintain were not kept, and records that were kept did not necessarily survive until today. We do know that, in a world where nations did not maintain careful accounting practices, or have "social safety nets" established, it took very little to create widespread economic turmoil.
02 February 2013
Compurgators
The ultimate character witness.
Throughout several centuries and many countries, establishing your innocence or trustworthiness in a court of law could be done by the use of compurgators. The word comes from Latin com (with) + purgare (cleanse; hence the modern word "purge").
If you were accused of wrongdoing, you would gather compurgators to appear for you in court. Ideally, you would find 12 of the most respected members of the community who would be willing to stand there and say that they believe you when you say you are innocent. Mind you, if you were found standing over a dead body with a bloody knife in your hand, compurgators were not likely to save you. This worked well when you were accused of cheating on a debt or stealing a spoon and hard evidence did not exist against you...unless you had friends who were determined to protect you.
The opportunities for abuse of such a system were rampant.
Henry II, or instance, in 1164 made sure that compurgation would not be allowed in felonies; he did not like the fact that a cleric (priest) might literally get away with murder in an ecclesiastical court by merely being defrocked, while the royal courts would use capital punishment for capital crimes. The use of compurgation in any way as a defense in England was eliminated from the court system in 1833.
Throughout several centuries and many countries, establishing your innocence or trustworthiness in a court of law could be done by the use of compurgators. The word comes from Latin com (with) + purgare (cleanse; hence the modern word "purge").
If you were accused of wrongdoing, you would gather compurgators to appear for you in court. Ideally, you would find 12 of the most respected members of the community who would be willing to stand there and say that they believe you when you say you are innocent. Mind you, if you were found standing over a dead body with a bloody knife in your hand, compurgators were not likely to save you. This worked well when you were accused of cheating on a debt or stealing a spoon and hard evidence did not exist against you...unless you had friends who were determined to protect you.
The opportunities for abuse of such a system were rampant.
Henry II, or instance, in 1164 made sure that compurgation would not be allowed in felonies; he did not like the fact that a cleric (priest) might literally get away with murder in an ecclesiastical court by merely being defrocked, while the royal courts would use capital punishment for capital crimes. The use of compurgation in any way as a defense in England was eliminated from the court system in 1833.
01 February 2013
Nicholas Oresme
Nicholas Oresme (c.1325-1382) likely came from humble beginnings; we assume this because he attended the College of Navarre, a royally funded and sponsored college for those who could not afford the University of Paris. He had his master of arts by 1342, and received his doctorate in 1356. He became known as an economist, philosopher, mathematician and physicist.
One of his published works was:
Livre du ciel et du monde
(The Book of Heaven and Earth)
In this work he discussed the arguments for and against the rotation of the Earth.
- He dismissed the notion that a rotating Earth would leave all the air behind, or cause a constant wind from east to west, pointing out that everything with the Earth would also rotate, including the air and water.
- He rejects as figures of speech any biblical passages that seem to support a fixed Earth or a moving sun. (Keep in mind even today we unanimously speak about the beauty of the sun setting when it's really the Earth rising!)
- He points out that it makes more sense for the Earth to move than for the (presumably more expansive and massive) heavenly spheres and Sun to move.
- He assures his readers that all the movements we see in the heavens could be accounted for by a rotating Earth.
- Then he assures the reader that everyone including himself thinks the heavens move around the earth, and after all he has no real evidence to the contrary!
Years later, Giordano Bruno (1548-1600) wrote his theories out in a way so similar to Oresme's that it is assumed he had access to Oresme's writing.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)