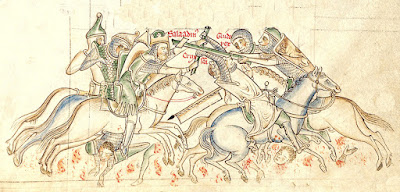
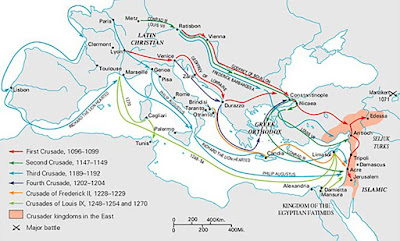
The Horns of Hattin is an extinct volcano whose twin peaks overlook Hattin in the Lower Galilee. In 1187, a battle took place between the forces of Saladin and Crusaders that was devastating for the Crusaders.
Saladin controlled much of the territory surrounding the Crusader forces and promised his people that he would drive the Christians from Jerusalem. Saladin had made a private treaty with the Franks in 1185 to give them Jerusalem if the Crusaders would stop waging further battles. There was peace until 1187 when a Muslim caravan was raided by Raynald of Châtillon. Saladin swore he would kill Raynald and sent a force to raid an area held by the Franks. The Templars lost about 150 knights and 300 foot soldiers in this battle (the Battle of Cresson), which was a severe blow to Frankish morale.
Guy was advised to move against Saladin, and on 3 July 1187, his forces started marching towards the Sea of Galilee (known at the time as Lake Tiberias). They were harried constantly nay Muslim archers, and along the way found little fresh water to replenish their supplies. The Muslim forces prevented them from reaching Lake Tiberias and fresh water, and set fires to the dry grass to annoy the Franks further with smoke and heat.
Three times the Frankish forces charged Saladin's, and three times they were beaten back, the third time being definitive. Many European nobles were taken captive that day. Guy of Lusignan and Raynauld of Châtillon were taken to Saladin. Saladin offered water to Guy, a sign that Guy would be treated well; Guy offered the water to Raynauld, but Saladin slapped it from his hand, charging Raynauld with breaking the truce. Raynauld was executed.
Guy of Lusignan was taken to Damascus as a prisoner (released in 1188). Two-hundred Templars and Hospitallers were beheaded, as were many others. A piece of the True Cross was taken from the Crusaders and sent to Damascus, about which I will have more to say next time.