16 April 2023
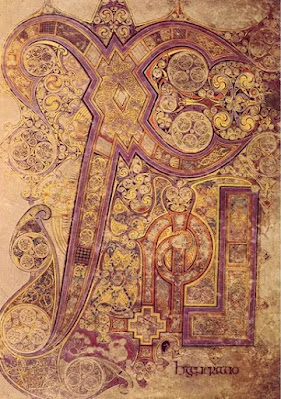
The Book of Kells
15 April 2023
The Lindisfarne Gospels
Best estimate is that the book was produced c.715-720 CE at the monastery at Lindisfarne by a monk (later bishop) named Eadfrith, who never quite finished the work. Written in Latin, the book is lavishly illustrated (the illustration is of a facsimile edition available here).
In the late 900s, in a monastery at Chester-le-Street—where the monks of Lindisfarne settled after fleeing the Vikings—a priest named Aldred decided the book needed an Old English translation, which he added between the lines of Latin. He also added a colophon to the book that tells us more about the production of it:
Eadfrith, bishop of Lindisfarne church, originally wrote this book for God and for St Cuthbert and—jointly—for all saints whose relics are in the island. And Æthelwald, bishop of the Lindisfarne islanders, impressed it on the outside and covered it ... And Billfrið the anchorite forged the ornaments which are on it on the outside and adorned it with gold and gems and with gilded-on silver-pure metal ...
The Gospels disappeared from view after the Dissolution of the Monasteries by Henry VIII, turning up later in the Cotton Library. The binding described above is no more, presumably lost during the time of Viking raids. A new binding wasn't added until 1852, arranged by the bishop of Durham.
The Lindisfarne Gospels is one of the most impressive books of its era—or perhaps of any other, except, of course, for the Gospel we're going to look at tomorrow. See you then.
14 April 2023
The Holy Island
The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle entry for the year 793 refers to the island as Lindisfarena, although around the same time Nennius' Historia Brittonum ("History of the Britons") calls it by a Welsh name, Medcaut, thought by later scholars to derive from Latin Medicata (Healing), due to medicinal herbs that grew there.
It became known as the Holy Island (Latin Insula sacra) in the 11th century because of Saints Aidan and Cuthbert. It was instrumental in the Christianization of Northumbria, and also sent a mission down to Mercia. Cuthbert was enormously popular and influential. An anonymous life of Cuthbert written between 685 and 704 is the oldest piece of English historical writing in existence.
The entry for the year 793 mentioned above is about the Viking raid on Lindisfarne. The entry reads:
In this year fierce, foreboding omens came over the land of the Northumbrians, and the wretched people shook; there were excessive whirlwinds, lightning, and fiery dragons were seen flying in the sky. These signs were followed by great famine, and a little after those, that same year on 6th ides of January, the ravaging of wretched heathen men destroyed God's church at Lindisfarne.
(January was not an ideal time for sea-born Viking raids; it is assumed that there was a "typo" and that 8 June was the date of the devastation.)
Alcuin later describes the destruction:
Never before has such terror appeared in Britain as we have now suffered from a pagan race ... The heathens poured out the blood of saints around the altar, and trampled on the bodies of saints in the temple of God, like dung in the streets.
Cuthbert's body and other relics were removed by the monks to save them from destruction.
With the arrival of the Normans after 1066, a Benedictine monastery was established by the first Norman bishop of Durham, William of St. Calais.
Back to the early years, however: something that came out of Lindisfarne in its pre-Viking heyday was the Lindisfarne Gospels, which I want to talk about next.
13 April 2023
Cuthbert's Travels
Cuthbert (c.635 - 687) was a very important saint in Northumbria, but his reputation was enhanced and expanded when Alfred the Great had a vision of Cuthbert that inspired him in his battles against the Danes. Alfred's house of Wessex became particularly devoted to the northern saint, making Cuthbert a saint for all of England. Preserving his remains was a necessity.
Initially buried at Lindisfarne, Danish invasions caused the monks to flee the island in 875, taking Cuthbert's bones along. Bede wrote that Cuthbert was put in a stone sarcophagus, but fortunately for the people in charge of moving him that was abandoned for a wooden coffin. After seven years of relocating to different sites, including Melrose, he was taken to Chester-le-Street, a market town in County Durham, where the body was interred and remained for 112 years at the parish church of St. Mary and St. Cuthbert.
In 995, the coffin was moved to Ripon, again because of the Danes. Upon its return to Chester-le-Street, the wagon carrying the coffin became stuck on the road at Durham. This was seen as a sign that the saint wished his remains to be in Durham, and he was taken to Durham Cathedral.
When William the Conqueror began the Harrying of the North to put down northern rebels, Bishop Ælfwine in 1069 tried to take Cuthbert's body back to Lindisfarne, but he was caught (and imprisoned, where he died).
In 1104, the coffin was opened and his relics taken to a new shrine built for him in Durham Cathedral. At this time a book was found, a Gospel of John called the Cuthbert Gospel; it is the oldest surviving book with its original binding.
During the Dissolution of the Monasteries by Henry VIII, Cuthbert's shrine was destroyed, but the relics survived interred at the site. A dig at the site in 1827 uncovered the relics and the remains of a wooden coffin (illustrated above), reconstructed from what pieces were salvageable.
All things considered, I am sure Cuthbert would have preferred to remain at Lindisfarne. What made the "Holy Island" so special is worth a closer look...next time.
12 April 2023
St. Cuthbert
The night of Aidan's death (651), Cuthbert had a vision that inspired him to become a monk. He advanced quickly, starting at a new monastery at Ripon, then becoming prior at Melrose Abbey in 662, followed in 665 by becoming prior at Lindisfarne. He was made a bishop in 684, but when nearing the end of his life he resigned that position.
Despite his exposure to Celtic Christianity for much of his youth, after the Synod of Whitby he had no trouble following the Roman system, bringing it to Lindisfarne when he was prior.
His reputation for piety and asceticism drew much attention, and he had many visitors despite his preference for a quiet life. He performed missionary work all over northern Britain. He was known for generosity to the poor and for performing miracles of healing, earning him the title "Wonder Worker of Britain." Bede wrote that he was buried in a stone sarcophagus to the right of the altar at the church in Lindisfarne; when the sarcophagus was moved behind the altar 11 years later (a more prestigious position), it was opened; his body was found perfectly preserved, "uncorrupted," a sign of his sainthood. This brought more pilgrims to Lindisfarne, and prompted many in need to pray for his intercession.
Lindisfarne, however, was not going to be Cuthbert's final resting place. He was going to be moved a few times due to Viking invasions, which I'll talk about next time.
11 April 2023
The Oldest Book
It is a "pocket-sized" Gospel of John from the 8th century, only 5.4' x 3.6" with 94 vellum folios (pages) and a leather binding/cover over wooden boards (pictured here). It was kept with other relics of St. Cuthbert at Durham Cathedral. When King Henry VIII dissolved the monasteries after 1536, it traveled probably through many hands until it finally landed at Stonyhurst College in Lancashire. It was on long-term loan to the British Library due to its value as an early example of book binding and its association with the Anglo-Saxon saint, Cuthbert of Lindisfarne. Eventually the British Library purchased it, so it is now part of their permanent collection. It is intended to be displayed alternately between the British Library and at Durham.
The reason we have such a well-preserved book is because it was not known to exist for several centuries. Cuthbert died in 687 CE; his coffin was moved more than once to protect it from Viking invasions. In 1104, the coffin was moved to Durham Cathedral for re-burying, and was opened for a glimpse of the venerable saint. That was when, four centuries after the death of Cuthbert, the gospel was found inside the coffin!
Initially thought to be Cuthbert's personal Gospel, it is now thought that it was placed in the coffin to be with him a few years after he died. Based on the form of writing, it is presumed to have been written between c.700 and c.730 and slipped into his coffin at a later date.
Who was Cuthbert? Why was he so important that someone wanted to give him a "gift" of a Gospel even after he died? And important enough that his coffin was moved several times to keep it safe? We'll take a look at him and his accomplishments next time.
10 April 2023
Parchment Production
The person who made parchment was a parchmenter. He would first have to acquire the raw material, which probably meant a trip to an abattoir to choose the best skins for use. Assuming they were completely unprepared, he had to gauge how the color of the fur indicated the final color of the parchment. White fur meant you would have lighter pages when all is said and done, but darker colors were probably more common. The skins might have holes in them from damage the animal did to itself or from tick bites.
The first step in preparation was to wash the skins in cold water. Skins were then commonly soaked in vats of water with lime for three to ten days, stirring regularly, after which they were laid out so they could be scraped to get the fur off. They were soaked in water for a couple more days after the scraping. The now waterlogged skin was stretched on a frame to dry flat. Strings attached the skin to pegs on a wooden frame; the pegs would be tightened to stretch the skin. You would not want to put holes in the skin for the strings, however, so the edge of the skin was rolled around pebbles and the end of the string tied around them.
Once dried, the skin was now scraped thin and smooth with a lunellum, a blade shaped like the crescent-moon so there was no sharp point that would accidentally pierce the skin. Rubbing with chalk would help to further smooth the result. Pre-13th century examples of parchment were thicker than later sheets, as the process was used to make thinner and thinner pages. These pages could then be written on and cut to be bound.
The development of parchment allowed books to last in good condition far longer than paper. So what's the oldest (medieval) book in good condition, and why was it in the coffin of a 7th century saint? For that story, you'll have to stay tuned.
09 April 2023
Books on Demand
Unlike the modern book store, however, you had choices that are not available today. Once you had determined that he did have access to a copy of the book you wanted, you had to decide on certain features.
Did you want parchment or paper? What quality of parchment (were holes okay)? What script did you want it produced with? Did you want illustrations? Since it was being made from scratch for you, you had options we cannot (and, fortunately, do not have to) imagine today. I've made the illustration a little larger than usual (I hope it shows clearly in your browser), so that you can see not only the samples of script being advertised by a 15th century bookseller, but also the names of the different scripts written above each sample in gold lettering. This is an advertising sheet produced by professional scribe Herman Strepel of Münster in 1447.
And if you were producing the book and looking for more business, why not include ads for your services? A Paris manuscript includes, on the last page, “If someone else would like such a handsome book, come and look me up in Paris, across from the Notre Dame cathedral.”
Not every "addition" to a book was an ad. A Middle Dutch chronicle includes the line “For so little money I never want to produce a book ever again!”
Book production employed different skilled tradesmen: the scribe himself, the illustrator, and the person who did the binding of the completed pages. Inks and paper or parchment had to be readily available, so those manufacturers were kept busy by demand, especially in university towns. In Paris, the Rue St. Jacques was where you'd find the producers of Latin textbooks, making it easy for students to know where to go to order needed materials for study. A lot more about medieval books is available on this blog.
Of course Gutenberg changed a lot of that, which is why I consider his innovation to be one of the markers that the Medieval period had truly ended. Gutenberg's press did not end the need for something on which to put the printed word, however. Next I'll talk about the production of parchment.
08 April 2023
Medieval Bookshops
“You swear that the books received by you shall be safely kept, exhibited and sold in good faith. You swear that you will not deny them nor conceal them, but that you will expose them at proper time and place. You swear that if you are consulted on the selling price of one or more books, you will give in good faith, reserving your proper commission, an estimation, i. e. , such a sum as you would voluntarily give on occasion. You swear that the price of the copy, and the name of the vendor (the person sworn), if required, shall be placed in some part of the book exposed for sale.”[link]
07 April 2023
John de Garlandia
Specifically, it describes a practice already in use, known as modal rhythm, which used the rhythmic modes. In this system, notes on the page are assigned to groups of long and short values based on their context. De mensurabili musica describes six rhythmic modes, corresponding to poetic feet: long-short (trochee), short-long (iamb), long-short-short (dactyl), short-short-long (anapest), long-long (spondee), and short-short (pyrrhic). Notation had not yet evolved to the point where the appearance of each note gave its duration; that had still to be understood from the position of a note in a phrase, which of the six rhythmic modes was being employed, and a number of other factors.Modal rhythm is the defining rhythmic characteristic of the music of the Notre Dame school, giving it an utterly distinct sound, one which was to prevail throughout the thirteenth century.[New World Encyclopedia]
Did a bookshop opener write this work? Evidence suggests that it was written in 1240, before John was born (he lived until 1320, so writing in 1240 was not possible), but his name is attached to it, leading to the assumption that he edited the work, or at least wrote later chapters of it. Some of the records of the time refer to John as magister, however, suggesting that he was a teacher at the University of Paris and not just a seller of books. How much he had to do with this work is unknown, but the connection made to it historically is accepted in the absence of other evidence.
For more on the history of musical notation, see here and here.
For information on bookshops in the Middle Ages, well, you'll just have to come back tomorrow.
06 April 2023
John of Garland
He left Toulouse around 1232 when the Cathars re-asserted themselves and university professors stopped being paid. He fled to the University of Paris, where Roger Bacon heard him lecture. It was this time in Paris that gave him his surname: he explains it is from the Rue Garlande in the neighborhood of the University.
There are over two dozen of his writings known (there are a few titles we know of, but have no extant copies). One was his Dictionarius (shown here), which was not a dictionary as we know it, but a textbook that attempted to teach Latin to French students at the University of Paris. Some credit Garland for the origin of the modern word "dictionary."
Besides works of instruction, he wrote poetry such as the Epithalamium beatae Mariae Virginis (“Bridal Song of the Blessed Virgin Mary”) and his account of the crusade against the Cathars, De triumphis ecclesiae (“On the Triumphs of the Church”). His hostility toward heresy was extended to Jews. To quote an author who wrote about this topic:
Although he never denied the possibility that conversion to Christianity could redeem the Jews, he thought it unlikely they would come over to the Catholic faith or remain steadfast in the religion. His invective was extreme by the standards of the time but was influential in that it appeared in many of his pedagogical works for adolescents and young men at the universities. [Journal of Medieval History, Vol.48, Issue 4]
Despite his time in France, his numerous writings were very popular in England, and were printed and re-printed in the 14th and 15th centuries.
Curiously, there was a second John of Garland who lived and wrote about the same time; this one was a music theorist, and will be our next topic.
05 April 2023
The Recording Demon
The notion of a "recording demon" was popular in the Middle Ages, and went from sermons to physical representations quickly. Here we see two men gossiping (from St. James' Church, Cristow, Devon), and no matter how close and secretive they are trying to be, right above their heads you can see the recording demon taking notes on what they are saying, to be used against them on Judgment Day.
The idea of a recording demon was known in Egyptian monasteries of the 4th century, and was said to visit churches and monasteries and write down the sins that he observed. This demon was ultimately given a name, Titivillus, and he became responsible to some for causing scribal errors. He was used in sermons about acedia, "spiritual sloth": churchgoers who engaged in idle chatter during the service, and priests who mumbled swiftly through the words of the service in order to get done faster.
Another representation of a demon collecting people's words is the "sack-filling demon" or simply "sack demon." Caesarius of Heisterbach mentions this one: a devil in a high place catching the words of people and putting them in a sack. Jacques de Vitry in his sermons mentions the sack demon with an over-filled sack, difficult to handle with the enormous number of inappropriate things said by folk.
The story of the deacon laughing in church was repeated and embellished over time. One version has the deacon criticized by the priest, who does not believe his story. Later, while asleep, he is exonerated when the Virgin Mary places the scroll of the demon's writings on his chest. The scroll proves to the priest that the deacon was telling the truth.
This is told in a poem by John of Garland, of whom I will say more tomorrow.
04 April 2023
The Demon Titivillus
At a time when fear of demons was common, they were "seen" everywhere: causing children to be ill, folk to go mad, cows to dry up, crops to fail, wells to go bad, etc.—they were constantly interfering with human life. One of them was considered the "patron demon of scribes" because he was blamed for errors in manuscripts. His name was Titivillus, sometimes Tutivillus, but in some of the earliest manuscript mentions, their middle letter is unclear and could be n or u/v, so it is written sometimes as Titinillus.
Despite the connection to Caesarius, and a reference in the writings of John of Wales, who died c.1285, as a demon who existed to introduce errors into scribal work, the Oxford English Dictionary's entry attributes the first reference to Peter Paludanus (c.1275 - 1342), who became Latin Patriarch of Jerusalem. The OED suggests the name of the demon might come from Latin titivillitium, a "mere trifle." Titivillus must have been looking over James Murray's shoulder, because Titivillus is clearly found in John of Wales' work long before Peter Paludanus would have been writing. In the Tractatus de Penitentia ("Tract on Sin"), we find
Fragmina verborum titivillus colligit horum
Quibus die mille vicibus se sarcinat ille.
Titivillus gathers up the fragments of these words
with which he fills his sack a thousand times a day.
He gets mentioned in a lot of medieval sermons as a reminder to be ever on guard against error and sloth. Titivillus became a character in medieval Mystery Plays. In the 15th century morality play Mankind, Titivillus is summoned by Mischief and other distractions to make Mankind's life difficult, but only after the audience is asked to pay extra money to make him appear (presumably his costume was suitably fabulous to charge extra). Titivillus' standing as a literary figure fades after that, and Shakespeare uses "Tilly-vally" a couple times when a character brushes off a complaint worthy of Titivillus' sack.
Concerning the phrase "fills his sack." This is not about inducing errors into manuscripts, but something else. Titivillus' career gets conflated with that of other popular medieval figures to watch out for: a "recording demon" and a "sack demon." That's an entirely different post.
Titivillus' presence can still be detected, such as in the fact that the OED (and I cannot believe I have never mentioned it and its mentor James Murray before) misses the earliest reference (but then, I am reading from the first edition; it has been updated). He influences my own work: although I proofread my post hours after writing it and being away, I still miss errors, which are found and shared by a very good friend; I know he is a good friend because he reads daily! (Come to think of it, that friend's name is Nick, and isn't "Old Nick" a name for the devil? Maybe he's trying to undo Titivillus' history of work?)
Well, more demons tomorrow.
03 April 2023
The Prolific Caesarius
Caesarius was the prior (an administrator of an abbey, but not the abbot) of the Cistercian Heisterbach Abbey in western Germany. He wrote Dialogus miraculorum ("dialogue of miracles"), in which a monk tells tales of 746 miracles by saints to a young novice. About 60 versions still exist that were made by hand, suggesting that it was almost as popular as Jacobus de Voragine's Golden Legend.
He also produced sermons, which he claimed he had to make public because monks asked for more detail on his statements. One of his books deals specifically with his interpretation of the phrase Ave praeclara maris stella ("Hail bright star of the sea"), a nickname for the Virgin Mary and a 9th century hymn found in old manuscripts in the Abbey of St. Gall and elsewhere.
In one of his works he wrote about the fairly recent sack of the town of Béziers during the Albigensian Crusade led by fellow Cistercian Arnaud Amalric. Supposedly, when Arnaud was asked how to distinguish between Cathars and Catholics in the town, he said Caedite eos. Novit enim Dominus qui sunt eius ("Slay them all, the Lord will know his own"). This is apocryphal, but is considered the origin of the oft-used phrase "Kill them all and let God sort them out." He also is known for a paradoxical maxim about monasteries: that discipline causes prosperity and then prosperity undermines discipline.
Caesarius complained that his writings were taken and distributed before they were finished and proofread. Perhaps it was in this context that he blamed a demon for errors in his works. That demon was Titivillus, and he will be the subject of my next post.
02 April 2023
The First Mass Murderer
Arnaud was a Cistercian (a branch of Benedictines), who became abbot of Cîteaux from 1202 to 1212. In 1204 he was sent by Pope Innocent III to attempt the conversion of the Albigensians who followed Catharism. His attempts to convert them to mainstream Catholicism did not work, and so his preaching turned to speaking out against them to those who would listen. This was followed by leading a Crusade against Catharism, the first major military operation of which was a 22 July 1209 attack on the town of Béziers in southern France.
In a letter to Innocent in August 1209, he describes the attack:
...while discussions were still going on with the barons about the release of those in the city who were deemed to be Catholics, the servants and other persons of low rank and unarmed attacked the city without waiting for orders from their leaders. To our amazement, crying "to arms, to arms!", within the space of two or three hours they crossed the ditches and the walls and Béziers was taken. Our men spared no one, irrespective of rank, sex or age, and put to the sword almost 20,000 people. After this great slaughter the whole city was despoiled and burnt...
The number 20,000 is clearly an exaggeration, but his description of the wholesale slaughter "irrespective of rank, sex or age" is likely to be more or less accurate. Because the sack of Bèziers apparently did not distinguish between Cathars and Catholics, Arnaud is reported to have said at the time "Kill them. For the Lord knows who are His."
This is considered the origin of an oft-repeated line: "Kill them all and let God sort them out." Arnaud's line was recorded 13 years later by Caesarius of Heisterbach, prior of a Cistercian abbey. Caesarius was not an eyewitness, never met Arnaud, and we have no proof that Arnaud actually said this, but some use the incident to refer to Arnaud Amalric as the first proponent of mass murder.
Arnaud was named archbishop of Narbonne in 1212, after which we hear little about him. He died on 29 September 1225.
As for his imaginative chronicler, Caesarius of Heisterbach, I'll tell you a little more tomorrow, as well as his identification of a particularly unhelpful demon.