24 October 2022
Simon Sudbury
23 October 2022
The Talbot Dog
22 October 2022
The Talbot Shrewsbury Book
The book is real. It is known as the Talbot Shrewsbury Book (also known as British Royal Library 15 E vi). It is a beautifully illustrated collection of 15 legends, stories, and other information written by several authors. Talbot commissioned it for Henry and Margaret's wedding in 1445. The book includes the illustration of Talbot presenting it to Margaret
Made of parchment bound in 440 pages, it is an example of Medieval/Renaissance book production at its height. The contents start out looking appropriate as a wedding gift for a queen, but near the end they become something else.
The Romance of Alexander the Great is followed by five tales of Charlemagne. After that are two Anglo-Norman prose romances, the story of King Horn and the Romance of Guy of Warwick (one of the most popular medieval romances). There follows a highly creative history of the Crusades.
The last 140+ pages seem to be less oriented toward a queen and more toward a queen's son, leading some to think it was intended for a future son of Margaret and Henry. There is a scholarly dialogue on war and battle, then a Mirror for Princes, a history of Normandy from the 8th century to 1217, a poem about chivalry, and the rules for the Order of the Garter.
If you look closely at the picture, you'll see a little white dog behind the kneeling Earl of Shrewsbury. This is the Talbot Dog, and it has its own place in history, which I'll talk about next.
21 October 2022
The Earls of Shrewsbury
The title "Earl of Shrewsbury" was first created in 1074 for a counselor of William the Conqueror, Roger de Montgomerie. He was given extensive lands to the west in order to keep an eye on the Welsh. Roger had two sons: Hugh and Robert. Hugh became the 2nd Earl at Roger's death, and Robert inherited his father's lands in Normandy. When Hugh died in 1098, Robert inherited the title. Robert then made the political miscalculation of joining Robert Curthose in one of his rebellions against King Henry I. The title Earl of Shrewsbury was discontinued.
Forward to the Hundred Years' War, and John Talbot, 7th Baron Talbot is distinguishing himself as a military commander. He is called the "English Achilles" and the "Terror of the French." He was an aggressive man both militarily and personally, not always making friends. His devotion to the cause of English rule over France was unquestioned. When he left the battlefields of France to return to England and request reinforcements in 1442, King Henry VI made him 1st Earl of Shrewsbury. He got the reinforcements he wanted, and went back to France.
The war was winding down, however, and England's chance of winning looking less likely. When in June 1443 he returned to England for more reinforcements, he was refused by the Council (they sent a different force under command of Edmund Beaufort, who would figure largely in the Wars of the Roses). Taken hostage in Rouen in 1449, he promised never again to fight against the French; he did, however, advise and command others, even if he himself did not use a weapon in battle.
He was killed at the Battle of Castillon, a decisive ending to the War. Supposedly his horse was injured and fell on him, enabling an enemy soldier to finish him off with a battleaxe. His son John Talbot became the 2nd Earl of Shrewsbury, a line of succession that continues to the present day.
"Second Creation" is the term used when a title that has become defunct because the line died out with no heirs or the title is revoked by the king's decree gets re-created for a new person. Many titles have needed a Second Creation or more.
Now, about that picture above: why is he on his knees, what is that in his hands, and to whom is he giving it? Tomorrow we talk about the Talbot Shrewsbury Book.
20 October 2022
Alton Castle
In the 1st century BCE there was an Iron Age fort on the site, but more continuity started when King Ceolred of Mercia built a wooden fortress there. The place was attacked by King Ine of Wessex in 716 in a battle so bloody that the location was called Slain Hollow (until Pugin turned it into an oriental water garden).
After the Conquest of 1066, the castle was rebuilt and enlarged in stone by the Norman noble Bertram de Verdun, who had been granted land in England by William. It stayed in the Verdun family through three generations of "Bertram de Verdun"s; then, in 1318, Joan de Verdun married Thomas de Furnival. Thomas died crusading in 1348, and the estate went to Sir John Talbot who married Furnival's daughter Maud. Talbot was created the first Earl of Shrewsbury (sort of; I'll explain later). Alton Castle stayed in the Talbot family; the 16th Earl of Shrewsbury was the owner during the 19th century expansion, after which the building was renamed Alton Towers.
In the 20th century the grounds were opened to the public, and now in the UK the phrase "Alton Towers" invokes images of an enormous theme park and resort that has been developed at the site.
But back to the first Earl of Shrewsbury. The first Earl of Shrewsbury was not the first; I'll explain how there were two "firsts" tomorrow.
19 October 2022
Augustus Pugin — Reviving the Middle Ages
He disapproved of the materialism of the Industrial Revolution, he designed according to "Christian principles," which to him meant medieval. He explained this in his 1836 book Contrasts, or, A Parallel Between the Noble Edifices of the 14th and 15th Centuries and Similar Buildings of the Present Day, Shewing the Present Decay of Taste.
He brought his "Gothic Revival" style to things other than buildings, and the pictures offer two examples of a chair and a table designed by him and inspired by what he might have called the "medieval aesthetic." I personally find his furniture and accessories odd. The holes in the chair don't match in my (admittedly limited) memory any design motif from the Middle Ages. The side table is even more odd. The quatrefoils hanging down—when they would have normally been oriented upward—seems to be adding architectural motifs into places where they don't quite fit in. Years ago, while visiting the Victoria and Albert Museum, I saw a Gothic Revival chair where the gothic pointed arch that enabled the larger windows of Gothic cathedrals was carved into the wood upside down.
As a fan of the European Middle Ages, I am glad that the 19th century saw value in the art and architecture of that earlier era. I think it possible that, at times, they went too far. (But perhaps that's just me.) An article in Architectural Review on the occasion of the bicentennial of his birth can tell you more.
I think it is better for me to stay focused on his architectural work, such as his castle. His Alton Castle had a long history before Pugin came along to rebuild it, which we'll look at tomorrow.
18 October 2022
Pewter
Pewter ware was made by melting and pouring into molds, which in the Middle Ages were often plaster or clay reinforced with calf hair. Adding a design was done by chiseling or etching with acid. Stamping a design was not always useful, since the pewter was soft enough that you would need to support it from the other side; the force of the stamp could easily deform the nice round shape of a goblet or tankard. (Stamping a flat plate would work.)
Pewter was turned into anything imaginable for daily use: plates, bowls, mugs, flatware, basins, measuring spoons and cups, ladles, goblets and cups and tankards, candlesticks (see picture for a 14th century example), teapots and sugar bowls and cream jugs. Pewter was so useful and common that regulations cropped up to ensure quality control.
The lead content is a concern, of course, and modern pewter designed for human contact contains no lead. Higher lead content produced darker pewter, so if handling an antique, the darker it is, the less you want it in contact with your skin. Lead toxicity was well-known to the Romans; they recognized that those who worked extensively with lead suffered the same cognitive symptoms. Colonial American higher quality pewter—a well-to-do person's dining room table, for instance—was likely lead-free (substitutes were antimony, brass, copper, or zinc), even though there was plenty of lower quality pewter being made using lead, especially in the kitchen.
Developments in glass-making and pottery, such as the introduction of porcelain—especially when Portuguese traders started bring back kaolin from China, allowing potters to make their own fine white "china"—made pewter less desirable. In the 19t century, however, there was a revived interest in England in medieval styles and art. I first mentioned the man responsible for this interest a decade ago; time to re-visit him ... tomorrow.
17 October 2022
Mining in Cornwall
The earliest evidence shows that tin was being mined in at least 2150BCE, the early Bronze Age. Copper was also found there, along with some arsenic, lead, silver, and zinc, but tin mining has been the most consistent use of the mines for millennia. When a small amount of tin is added to copper, the resulting bronze is much harder than either and more useful. This made tin a more useful commodity than just using tin on its own, and a tin trade with the Mediterranean started long before even the Roman Empire. Herodotus mentions an area called the Cassiterides, the "tin islands," and Cornwall is thought to be the likeliest spot.
One of the oldest mines in Cornwall is the Ding Dong mine (the name may refer to the "head of the lode"). The picture above is a shaft at the Ding Dong. A local legend claims that the mine was visited by Joseph of Arimathea, tin trader and uncle to Jesus, who visited the mine with the young Jesus; not his only trip to Britain, since he later founded Glastonbury Abbey, etc. (There is, of course, no evidence, but that's what legends are.)
Curiously, Domesday Book doesn't mention Cornwall tin, but Henry II acknowledged it when he granted to Dartmoor, another mining location,
all the diggers and buyers of black tin, and all the smelters of tin, and traders of tin in the first smelting shall have the just and ancient customs and liberties established in Devon and Cornwall.
This indicates that Cornwall mining was "ancient" as of Henry's reign. Henry's son John granted a charter for the miners' rights, establishing stannaries that allowed the tin-mining community to administer its own laws, etc.
The mines produced an enormous amount: 650 tons in 1337, falling to "only" 250 tons during the Black Death, but rising to 800 tons by 1400.
Demand for tin decreased in the 20th century. Increased recycling efforts, as well as the use of aluminum for containers and the development of protective polymer lacquers to coat food containers hastened the closing of tin mines as unprofitable. One of the last tin mines in Cornwall to close was the South Crofty mine in 1998, Europe's last tin mine.
Fear not for Cornwall mining, however! The 21st century is finding reasons to re-open defunct Cornish mines for a substance as important to our time as tin was to the Bronze Age: lithium, an element vital to our battery-operated world. (Here is a link to National Geographic article.)
Going back to the Middle Ages, however, I want to talk about another substance, made with tin, that was so associated with daily use in the Middle Ages that a 19th century revival of interest in the Middle Ages made this substance much in demand. Check back tomorrow and we'll learn more about the lovely, useful, and toxic pewter.
16 October 2022
Stannaries
Tin was so important that a body of law was developed to deal specifically with stannaries. King John in 1201 gave the tin miners of Cornwall the Stannary Charter: the right to prospect for tin anywhere, to be exempt from standard taxation, and to have their own stannary courts in the case of law-breaking. King Edward I in 1305 confirmed these rights, as did Edward III when he created the Duchy of Cornwall in 1337. Crockern Tor, pictured above, was the site of the Stannary Parliament, representing the tin industry.
Tin mining pre-dated the Middle Ages in Cornwall. When the Romans arrived, it was already thriving. Diodorus Siculus in 44BCE wrote the earliest reference to Cornwall we know:
The people of that promontory of Britain called Belerion [west Cornwall] are friendly to strangers and, from their contact with foreign merchants, are civilised in their way of life. They carefully work the ground from which they extract the tin.
This whole system of special privilege, etc., existed until the Tin Duties Act of 1838.
The history of mining in Cornwall was far more extensive than dealing with tin, even tied to a Biblical legend. I'll tell you more next time.
15 October 2022
Isabella of Angoulême
It was not to be, however: King John of England came looking for a wife who could give him heirs, which was not going to happen with his first wife, Isabella of Gloucester. He settled on Isabella of Angoulême, annulled his first marriage, and married for the second time on 24 August 1200.
Isabella was still a child, and John treated her carefully, so it was not until 1 October 1207 when she was about 20 years old that she gave birth to a son and heir, who would become Henry III. She bore John a total of five children.
Henry was nine when John died, and Isabella swiftly arranged to have him crowned king. Unfortunately, John had lost his crown and much of his treasury, so she provided her own queen's circlet as part of the ceremony. By this time, she was already Countess of Angoulême (her father had died in 1202), so a year after the coronation, she left Henry in the care of his regent, William Marshal, and went to her lands in Angoulême.
In an interesting parallel, her daughter Joan (born 1210) was being raised in the Lusignan court and had been betrothed to Hugh X of Lusignan, son of the man to whom Isabella was originally betrothed. Hugh, however, seeing that Isabella's beauty had not diminished (she was only in her 30s), proposed to the woman who had long ago been promised to his father. They were wed in the spring of 1220. A different marriage was arranged for Joan.
As it turns out, the king's council in England reserved to itself the power to determine whether and to whom a queen dowager should marry; after all, she held lands due to her dead husband, and had a pension from the council. They objected to her marriage to Hugh that was done without their consent, so they canceled her pension and confiscated her English possessions. They wrote to the pope, asking for her to be excommunicated, but ultimately decided to negotiate with her for a swifter conclusion, because Isabella was keeping Joan with her, preventing the alternate marriage that was arranged to the King of Scotland. The council decided to allow her some financial support, like the stannaries in Devon.
Isabella had a difficult time adjusting to life as less than a queen. She and her husband tried uniting some of the French nobles against Louis IX. She encouraged Henry III when he invaded Normandy in 1230 (but could not provide him any military support). An attempt to poison King Louis IX by two cooks was foiled in 1244, but the cooks admitted they were paid by Isabella. She fled to Fontevrault Abbey for sanctuary ahead of the king's men, where she died on 4 June 1246. She was buried outside the abbey. Henry III visited the abbey later and objected to her burial outside. He had her moved inside, near Henry II and Eleanor of Aquitaine.
All of her children—five with John, nine with Hugh—survived to adulthood and had titles and good careers, any of whom would be interesting to look at next. I think, however, the "stannaries in Devon" wants explanation, and will be a nice respite from political marriages. See you next time.
14 October 2022
Isabella of Gloucester
Henry arranged betrothal to Isabella of Gloucester, but only after disinheriting her sisters so that all Gloucester lands would be hers on her father's death. This was in 1176, when John was nine and Isabella was only three or four years old. Both were great-grandchildren of Henry I, meaning the marriage was forbidden due to the laws of consanguinity. The wedding did not take place until 29 August 1189, at which John became Earl of Gloucester.
The Archbishop of Canterbury, Baldwin, placed the Gloucester lands under interdict—meaning no one living there could partake in any Catholic services—due to the violation of consanguinity laws. An appeal to (antipope) Pope Clement III for a dispensation. This was granted, on the condition that the two abstained from sex. This explains why 10 years of marriage produced no children.
John pursued the consanguinity prohibition when it suited him—which it did after he became king. Wanting an heir, and not being interested in having them with Isabella, he annulled the marriage on the grounds of too-close blood ties. He put Isabella in "honorable confinement" at Winchester with an allowance for her comfort. John's lack of sensitivity to the feelings of others—and, after all, there is no sign that he cared for Isabella at all except for the political advantage—had a "task" for her. When John re-married, to a twelve-year-old Isabella of Angoulême, he lodged his new bride at Winchester in the care of his first wife, increasing her allowance from £50 to £80 pounds because she was hosting a queen. The second Isabella stayed with the first until a few weeks before she gave birth to the future King Henry III.
Eventually he found a new marriage for Isabella: in 1214, the Earl of Essex, Geoffrey de Mandeville paid to John 20,000 marks for the privilege to marry Isabella. He was a much younger man, but he died two years later. Unfortunately, because at the time of his death he had been rebelling against John, John confiscated all his lands, which included Isabella's Gloucester lands.
Now a poor widow, she married again a year later, to Hubert de Burgh who became the Chief Justiciar under John and John's son, Henry III. Sadly, she died only a month after marrying Hugh. She was interred in Canterbury Cathedral.
Now, about that second wife also called Isabella: let's learn more about her next.
13 October 2022
John's Marriages
For one...well, we don't know enough about Isabella to know when she was born, but one estimate is 1188, making her 12 years of age. Still, she would be Countess of Angoulême in her own right when her father died (which he did, in 1202). Also, she was the niece through her mother of the current Latin Emperor of Constantinople, Peter II of Courtenay.
The other—well, one other—issue was that John already had a wife: Isabella, Countess of Gloucester. He managed to have that marriage annulled on the grounds that, as his cousin, he never should have married her in the first place, and in fact had failed to get the proper papal dispensation to do so, considering the current laws of consanguinity (they would change the same year that John would sign the Magna Carta, 1215). Fortunately for John, Isabella complied with there annulment, even though he kept the lands he had received through their marriage.
Back to the second Isabella: she had already been betrothed to Hugh IX le Brun, Count of Lusignan (and remember that Roman numeral; we will be coming back to it in the post after next). Her father decided that his daughter would be better off as a queen than as a Countess of Lusignan, so he agreed to the change in husbands for her. John might have made amends with the Lusignan's, but instead chose to treat them with contempt. This motivated an uprising by the Lusignan and their supporters which John had to suppress. Philip II of France also took the Lusignan snub as an excuse to confiscate the Angoulême lands.
So John's choice did not have all positive results, and rather than make inroads into France through marriage, he alienated a powerful family and lost more lands to Philip.
The second Isabella provided John with something the first one never could, however: heirs, including the next king, Henry III. Here's a good question, though: John was married to his first wife for 10 years. Why did they produce no heirs? The reason is simple: the couple was forbidden to have sexual intercourse. I'll explain that tomorrow.
12 October 2022
The Angevin Collapse
This should not have been a surprise. John had rebelled unsuccessfully against Richard's administration while Richard was on the Third Crusade. In the present case, the loss of Richard created an opportunity for Philip II of France to take some of England's possessions on the continent, Évreux and the Vexin. The nobles of Anjou, Maine, and Touraine supported Arthur. John did, however, have the support of Aquitaine and Poitou thanks to his mother, Eleanor of Aquitaine, as well as Normandy. After being declared Duke of Normandy, he sailed to England where he was crowned in Westminster on 27 May.
Although England was largely secure, possessions in France were constantly the target of Philip II. John was forced into treaties with Philip in order to stop the hostilities. The Treaty of Le Goulet in 1200 saw John paying Philip 20,000 marks, giving up lands in Auvergne and Berry, giving up on the areas of Normandy that had been seized by Philip, and giving up his alliance with the Holy Roman Empire, who occasionally was a rival of France. The illustration shows via shades of red the dwindling authority of the Angevins.
John then decided to make a politically advantageous marriage, but there were two problems with that: one is that he was already married, and the second that John's decisions were almost always the wrong ones. Stay tuned.
11 October 2022
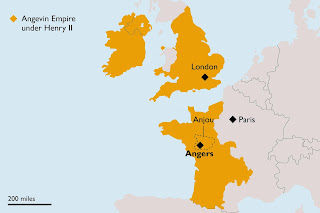
The Angevin Empire
Well, England, of course, in which Henry had his grandest title of king, and also parts of Ireland and Wales. Through Henry's father, Geoffrey of Anjou, he was also Count of Anjou. Also, since Geoffrey took over Normandy not long before, Henry was Duke of Normandy. Moreover, because Henry married Eleanor of Aquitaine in 1152—who divorced the King of France to do so—he had Aquitaine.
The term "Angevin" was coined in 1887 by a British historian, based on "Anjou." Henry and his successors (sons Richard and John and John's son Henry III) would refer in documents to "our kingdom and everything subject to our rule whatever it may be" and never called it an empire or referred to themselves as Angevin. Technically, they were all Plantagenets.
Plantagenet was Geoffrey of Anjou's nickname. The plantagenet was the common broom, a flowering plant with bright yellow blossoms. Geoffrey was also known as Geoffrey the Handsome or the Fair. Perhaps his hair was lighter than typical, and the comparison to the golden flowers of the broom prompted the nickname. Even so, like the term "Angevin," it wasn't until Richard, 3rd Duke of York adopted Plantagenet as his family name during the Wars of the Roses that the term become attached to the whole hereditary line. It seems that Richard was linking himself to his ancestor Geoffrey in order to emphasize his proper place in the line of succession.
Extensive holdings on the continent (and perhaps spite, since Eleanor had abandoned being queen in France to become Queen Eleanor of England), made France a little hostile to the Angevin Empire. The problem created by Duke William of Normandy when he became King William of England in 1066 remained: how does a king of a country (England) react when he is likewise a lesser title (duke, count) in another country (France) and therefore subordinate to a king? That political oddity would define the English-French relationship for centuries.
It also calls into question the term "empire." To truly be an empire requires a centralized government and consistent laws and regulations throughout the territories. The varying laws and customs of the various Angevin territories were at odds with this definition.
Whether it was an empire like the Roman Empire or the medieval Holy Roman Empire, it didn't last more than a generation or two. Its demise will be the subject of the next post.
10 October 2022
Empress Matilda
Matilda did not take well to Stephen's usurpation. She was not, after all, an idle daughter waiting for her moment to shine: by this time, she was Empress Matilda by virtue of marriage to Holy Roman Emperor Henry V (shown above in a 12th century chronicle). (And who would believe it? Henry V tried to usurp the throne from his father, Henry IV.)
Henry V had died 10 years prior to the current crisis, but Matilda retained the title Empress. Her father recalled her to Normandy and arranged marriage to Geoffrey of Anjou to protect his southern border. (Blois was also on the southern border of Normandy; perhaps if he had arranged a different marriage...?) From here she could make plans to assume the English throne, kicking off a period called The Anarchy.
Stephen's reign was not without trouble. Not everyone approved of him personally, or of his seizing of the throne after pledging loyalty to Henry's daughter. In 1139 she left Geoffrey to conquer Normandy while she crossed the English Channel to take the throne from Stephen. She and her half-brother Robert of Gloucester visited her step-mother Adeliza, which caused Stephen to react. Afterward, she and Robert, with support from her uncle, King David I of Scotland, raised an army and captured Stephen at the Battle of Lincoln in 1141.
The next step was to be crowned at Westminster, but the people of London were against her and prevented it. She was never considered a Queen, not even for a moment. Her title in royal listings is Domina Anglorum, "Lady of the English." Stephen's supporters captured Robert, and Matilda agreed to exchange him for Stephen.
Although she had control over much of south-west England, Matilda returned to Normandy in 1148 (now under her husband's control), leaving her eldest son to continue the war. Other factors were at play: she was living in a castle that she took from the bishop of Salisbury; Pope Eugene III threatened her with excommunication if she did not return it.
The war became a stalemate, and the stalemate become the 1153 Treaty of Wallingford (or Westminster, or Winchester: all three are used), formally ending The Anarchy and agreeing that Matilda's son would become king upon Stephen's death, which obligingly happened a year later. Henry became King Henry II of England, starting the Angevin Empire.
I'd like to talk about the impact of the Angevin Empire next, but if you want more detail on The Anarchy you can check out posts from 10 years ago: Parts One, Two, and Three, along with this.)