27 February 2023
The Umayyad Caliphate
14 January 2022
The Battle of Hattin
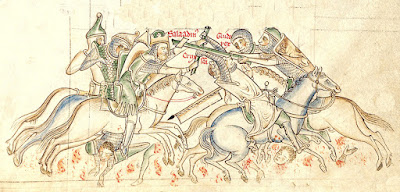
The Horns of Hattin is an extinct volcano whose twin peaks overlook Hattin in the Lower Galilee. In 1187, a battle took place between the forces of Saladin and Crusaders that was devastating for the Crusaders.
Saladin controlled much of the territory surrounding the Crusader forces and promised his people that he would drive the Christians from Jerusalem. Saladin had made a private treaty with the Franks in 1185 to give them Jerusalem if the Crusaders would stop waging further battles. There was peace until 1187 when a Muslim caravan was raided by Raynald of Châtillon. Saladin swore he would kill Raynald and sent a force to raid an area held by the Franks. The Templars lost about 150 knights and 300 foot soldiers in this battle (the Battle of Cresson), which was a severe blow to Frankish morale.
Guy was advised to move against Saladin, and on 3 July 1187, his forces started marching towards the Sea of Galilee (known at the time as Lake Tiberias). They were harried constantly nay Muslim archers, and along the way found little fresh water to replenish their supplies. The Muslim forces prevented them from reaching Lake Tiberias and fresh water, and set fires to the dry grass to annoy the Franks further with smoke and heat.
Three times the Frankish forces charged Saladin's, and three times they were beaten back, the third time being definitive. Many European nobles were taken captive that day. Guy of Lusignan and Raynauld of Châtillon were taken to Saladin. Saladin offered water to Guy, a sign that Guy would be treated well; Guy offered the water to Raynauld, but Saladin slapped it from his hand, charging Raynauld with breaking the truce. Raynauld was executed.
Guy of Lusignan was taken to Damascus as a prisoner (released in 1188). Two-hundred Templars and Hospitallers were beheaded, as were many others. A piece of the True Cross was taken from the Crusaders and sent to Damascus, about which I will have more to say next time.
06 May 2013
Damascus - Some History
دمشق.
Dimishe'.
al-Shām.
The City of Jasmine.
"Oldest continuously inhabited city in the world."
Damascus.
It was founded in the 3rd millennium BCE and (according to the Unesco World Heritage site) "has some 125 monuments from different periods in its history."
When Imad al-Din Zengi, the Prince of Mosul, laid siege to Damascus in 1138, Damascus resisted by allying with the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem (ruled at the time by Fulk V of Anjou [1089-1143]). The admirably tolerant Seljuq-Christian alliance turned back their common enemy. It was this conflict that prompted Raymond of Poitiers, Prince of Antioch, to send Bishop Hugh of Jabala to Pope Eugene III for aid. It was Hugh at the court of Pope Eugene whose mention of a Nestorian priest-king in the East started the legend of Prester John.
Saladin, the noble foe of Richard Lionheart, founded the Ayyubid dynasty, Muslim Kurds who ruled an independent Damascus. Saladin allowed pilgrimages to Jerusalem, with the understanding that the Crusaders would return home after fulfilling their Crusading vows. After Saladin's death in 1193, Damascus was ruled sometimes by Ayyubids from Damascus, sometimes by Ayyubids from Cairo.
By this time, Damascus was one of the western endpoints of the Silk Road. Damascus itself was known for crafts and cloth, and the cloth called damask was a specialty.
Independent Ayyubid rule ended in 1260 with a Mongol Invasion; when the Mongols left, Damascus was reduced to being a provincial capital of the Mamluk Empire of Egypt. A few generations later, the Black Death killed up to 50% of the population.