Tradition says that Brigid founded a monastery at Kildare (Cill Dara, "church of the oak"), with seven companions. She became a "consecrated virgin"; that is, she pledged to live a life of virginity as a bride of Christ. This was confirmed (according to the stories) by either a bishop who became St. Mac Caille or by Saint Mél of Ardagh (a nephew of St. Patrick by Patrick's sister Darerca).
Brigid invited a hermit, Conleth from Connell, to help her, and they founded two institutions: one for women and one for men. Conleth became the first bishop of Kildare. Kildare was ruled for hundreds of years by co-equal abbess-bishops and abbot-bishops, became an important center of religious learning, and developed into a cathedral city.
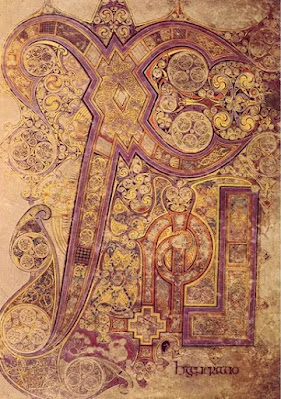
Conleth, who was a metalsmith and illuminator, oversaw a school of art at Kildare. A Gospel book made there was praised by Gerald of Wales in the 12th century. His description of it matches what we now know as the Book of Kells.
Miracles attributed to Brigid include turning water to beer, calming the wind and rain, and healing wounds. A more unusual miracle took place when she asked the King of Leinster for the land to build the monastery and was denied. After praying, she asked the king if he would grant her as much land as her cloak would cover. The king, of course, agreed. She handed her cloak to four women, asking them to each take a corner and run off in the four cardinal directions. The cloak expanded more and more, threatening to cover hundreds of acres.
The panicked king asked what she was doing, and Brigid told him she intended to cover his whole kingdom in response to his stinginess. He pleaded with her to call the women back and he would give her a suitable plot of land.
Brigid's Feast day is 1 February, the same date as the pre-Christian festival of Imbolc that heralds the start of spring, and involves weaving Brigid crosses. I want to talk about the Brigid cross tomorrow, and whether it is a clue to Brigid's existence as, not a saint, but a goddess. See you then.